For those who possess an unwavering passion for fostering a global paradigm shift towards a more sustainable and ethical future, the mere thought of embracing an alternative dietary lifestyle triggers a sense of empowerment and purpose. Alas, one particular aspect of this transformative journey lies in the realm of minimizing the consumption of a certain type of protein-laden sustenance, a fervor shared by a growing number of individuals seeking to create a significant impact on our planet's well-being.
In a world that demands innovative solutions, the aspiration to decrease reliance on the habitual devouring of red meat transcends being a mere fleeting fancy. Instead, it thrives as a harbinger of a more balanced and compassionate world, urging individuals to embark on an intellectual exploration of alternative dietary choices. This revolution, fueled by a fervent desire to protect the environment, safeguard animal welfare, and enhance personal health, mirrors the individual's ability to adapt and evolve in the wake of changing societal norms.
Steering clear of convention, this article delves into the vast expanse of culinary creativity and deep-rooted traditions that exist beyond the realm of red meat consumption. Through the exploration of mouthwatering alternatives, savory substitutes, and ingenious cooking techniques, we shall expose the reader to a bountiful array of possibilities, satisfying both the body and the soul.
Now, envision a world where vibrant salads dazzle the palate with an exhilarating burst of flavors, where plant-based proteins succulently substitute the carnivorous counterparts, and where exotic spices and herbs tantalize the senses with each aromatic waft. Prepare to embark on a culinary odyssey that not only celebrates the gathering of people around the dinner table but also serves as a catalyst for fostering empathy towards the environment and its inhabitants. For within this transformation, we find the power to transcend fleeting dreams and transform them into palpable realities, one mindful bite at a time.
The Environmental Impact of Consuming Meat
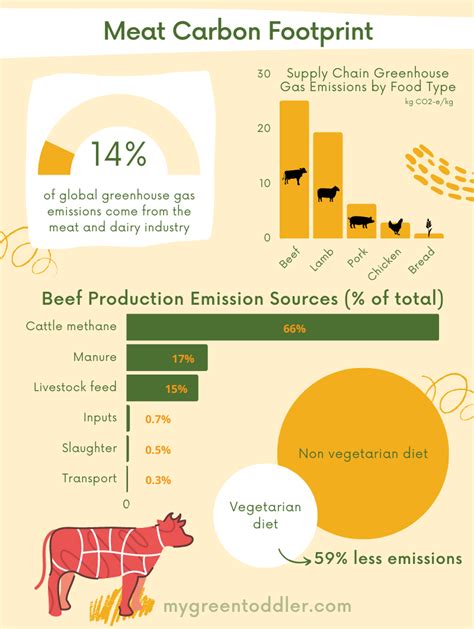
As awareness of the consequences of meat consumption on the environment continues to grow, it is crucial to delve into the various ways in which red meat consumption affects our planet. This section aims to explore and shed light on the ecological implications of consuming red meat, presenting a range of environmental issues that arise as a result.
1. Deforestation: The livestock industry is a major driver of deforestation, as vast stretches of land are cleared to make way for grazing animals and to cultivate feed crops. This process destroys invaluable ecosystems and contributes to the loss of biodiversity.
2. Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Red meat production is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly due to the release of methane from livestock digestion and manure. These emissions contribute to global warming and climate change, exacerbating the existing environmental crisis.
3. Water Scarcity: The meat industry places a substantial strain on water resources. From the vast amounts of water required to grow feed crops to the water utilized in the rearing and processing of livestock, red meat consumption contributes to the increasing scarcity of water worldwide.
4. Soil Degradation: Intensive livestock farming practices contribute to soil degradation through overgrazing, excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides, and the associated runoff. This leads to the loss of soil fertility, erosion, and contamination of water bodies.
5. Waste and Pollution: The production and processing of red meat generate significant amounts of waste, including animal manure, which can contaminate soil and water sources if not properly managed. Furthermore, the use of antibiotics in livestock farming contributes to the issue of antibiotic resistance in both humans and animals.
By understanding the environmental impact caused by consuming red meat, individuals can make informed choices to reduce their meat consumption or opt for more sustainable alternatives. The next section will explore strategies and practical steps to help make the dream of reducing red meat consumption a reality.
Exploring the Ecological Impact of Excessive Consumption of Beef
In the quest for a sustainable future, it is crucial to examine the ramifications of overindulging in beef, a widely consumed meat worldwide. This section delves into the ecological consequences that arise as a result of the surplus beef consumption, shedding light on the toll it takes on the environment.
- Land Degradation: The extensive demand for red meat necessitates vast areas of land for livestock production. This intense pressure on land resources leads to deforestation, habitat loss, and soil degradation. The conversion of forests and grasslands into farmland exacerbates the loss of biodiversity and disrupts delicate ecosystems.
- Water Scarcity: The production of red meat is an immensely water-intensive process. From growing animal feed to the actual livestock farming, substantial amounts of water are required. Consequently, excessive beef consumption contributes to the depletion of freshwater resources, aggravating the global water scarcity crisis.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The livestock industry, primarily beef production, is a substantial contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Methane, a potent greenhouse gas released during enteric fermentation in cattle, significantly amplifies the climate change crisis. Additionally, the energy-intensive processes involved in production, processing, and transportation of red meat further augment carbon emissions.
- Water Pollution: Widespread beef production involves the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides to support the cultivation of animal feed crops. These chemicals infiltrate water bodies, leading to contamination and eutrophication, ultimately disrupting aquatic ecosystems and endangering the organisms that depend on them.
- Waste and Pollution: The excrement generated by the livestock industry is a significant source of environmental pollution, contributing to water pollution and emitting greenhouse gases. Inadequate waste management practices further exacerbate the adverse impact on the environment.
By examining the environmental consequences associated with excessive beef consumption, it becomes evident that reducing red meat intake is crucial for a sustainable future. Understanding the intricate relationship between our dietary choices and the environment can pave the way towards adopting more sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives.
Importance of Health Considerations in Reducing Red Meat Intake

With growing awareness about the potential health risks associated with excessive red meat consumption, it is essential to consider the impact of reducing red meat intake on overall health and well-being. In this section, we will explore the various health considerations that should be taken into account when aiming to decrease red meat consumption. By understanding these aspects, individuals can make informed decisions about their dietary choices and improve their long-term health outcomes.
Enhancing Cardiovascular Health
One of the primary health benefits of reducing red meat intake is the potential to improve cardiovascular health. Studies have linked excessive consumption of red meat with an increased risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. By incorporating healthier alternatives such as lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into one's diet, individuals can decrease their risk of developing these conditions and promote a healthy heart.
Lowering Cancer Risks
Another significant health consideration is the potential reduction in cancer risks associated with decreasing red meat consumption. Some studies suggest that regular consumption of red meat, especially processed varieties, may increase the risk of colorectal, prostate, and breast cancers. By opting for plant-based proteins, individuals can potentially lower their risk of developing these types of cancers and promote better overall health.
Weight Management and Metabolic Health
Reducing red meat intake can also play a crucial role in weight management and metabolic health. Red meat is often high in calories, saturated fats, and cholesterol, which can contribute to weight gain and metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes. By choosing leaner protein sources and incorporating more plant-based options, individuals can achieve a healthier weight, improve their insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of obesity-related complications.
Improved Nutrient Profile
By reducing red meat intake and diversifying one's diet, individuals can also enjoy an improved nutrient profile. While red meat can be a source of essential nutrients like iron and vitamin B12, excessive consumption can lead to imbalances and deficiencies in other crucial vitamins and minerals. Incorporating a range of plant-based proteins, whole grains, and fruits and vegetables can provide a wider range of nutrients, enhancing overall health and well-being.
In conclusion, considering the various health implications of reducing red meat intake is essential when aiming to make healthier dietary choices. By focusing on cardiovascular health, cancer prevention, weight management, and improving nutrient profiles, individuals can pave the way for a healthier lifestyle and reduce their reliance on red meat as a significant protein source.
Discovering the Health Advantages of Reducing Intake of Beef and Similar Products
Exploring the potential health benefits associated with the reduction of beef and other comparable products unveils a dynamic field of research aimed at improved well-being and longevity. By understanding the positive impacts of lowering red meat consumption, individuals can make informed choices that align with their goals for healthier lifestyles.
One key advantage of minimizing the intake of red meat is promoting heart health. Numerous studies have shown a correlation between excessive consumption of red meat and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. By opting for alternative sources of protein such as poultry, seafood, legumes, and plant-based options, individuals can significantly reduce their consumption of saturated fats and cholesterol, leading to a healthier heart.
Additionally, reducing red meat consumption can contribute to weight management and overall weight loss. High in calories and often associated with weight gain, regular intake of red meat can hinder efforts to maintain a healthy body weight. By replacing red meat with leaner protein sources and incorporating a variety of vegetables and fruits into their diet, individuals can actively support their weight management goals.
Furthermore, decreasing red meat consumption is linked to a lower risk of certain types of cancers, particularly colorectal cancer. Various compounds found in red meat, such as heme iron and heterocyclic amines produced during cooking, have been associated with an increased risk of developing cancer. By emphasizing a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthier protein options, individuals can reduce their exposure to potentially harmful compounds and enhance their overall cancer prevention strategy.
In conclusion, comprehending the manifold health benefits tied to the reduction of red meat intake provides individuals with the knowledge necessary to make conscious choices about their dietary habits. Improved heart health, enhanced weight management, and a reduced risk of certain cancers are just a few of the advantages associated with minimizing red meat consumption and pursuing alternative protein sources. By making informed decisions, individuals can prioritize their well-being and work towards a healthier and more fulfilling lifestyle.
Practical Tips for Shifting to a Reduced Intake of Beef and Pork

Transitioning to a diet with a decreased emphasis on red meat can be a fulfilling and sustainable choice for improving personal health and promoting environmental conservation. In this section, we will explore some practical strategies and tips to help individuals make a successful transition towards consuming less beef and pork, while still maintaining a nutritionally balanced diet.
1. Explore Plant-Based Protein Sources
One of the first steps in reducing red meat intake is to explore alternative sources of protein, such as legumes (beans, lentils, and peas), tofu, tempeh, and seitan. These plant-based protein options can provide the necessary nutrients and amino acids that are commonly found in red meat.
2. Incorporate More Seafood and Poultry
Another way to reduce reliance on red meat is to incorporate more seafood and poultry into your meals. Fish, shrimp, chicken, and turkey are excellent sources of protein and can be prepared in various delicious ways. Adding variety to your diet with these leaner meat options can help satisfy your cravings while reducing red meat consumption.
3. Experiment with Meatless Meals
Challenge yourself to explore the world of meatless meals by experimenting with vegetarian and vegan recipes. Incorporating more plant-based dishes into your weekly meal plan can be an exciting and flavorful journey. It can also be an opportunity to discover new tastes and textures.
4. Gradual Reduction Instead of Abrupt Elimination
Instead of completely eliminating red meat from your diet overnight, consider gradually reducing your intake over time. Start by choosing one or two days each week to be meat-free. As you become comfortable, you can progressively increase the number of meatless days in your week. This approach can help make the transition more manageable and sustainable in the long run.
5. Plan Ahead and Be Prepared
Meal planning and preparation can be essential when transitioning to a reduced red meat diet. By planning your meals in advance and having the necessary ingredients on hand, you are less likely to revert to old habits. Having a well-stocked pantry with a variety of plant-based ingredients ensures that you can easily whip up nutritious meals without relying on red meat.
By incorporating these practical tips into your lifestyle, you can successfully embrace a reduced red meat diet and contribute to a healthier and more sustainable future for both yourself and the planet.
FAQ
Why is reducing red meat consumption important?
Reducing red meat consumption is important for several reasons. Firstly, excessive consumption of red meat has been linked to an increased risk of various health conditions, including heart disease, certain cancers, and diabetes. Additionally, the production of red meat has a significant impact on the environment, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. Therefore, reducing red meat consumption can not only improve personal health but also help mitigate the adverse effects on the planet.
What are some alternatives to red meat that can be incorporated into a diet?
There are plenty of alternatives to red meat that can be included in a balanced diet. Plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, and seitan are excellent options. Additionally, incorporating more fish, poultry, and eggs can provide lean sources of protein. It is important to ensure a variety of protein sources to meet nutritional needs.
How can I gradually reduce my red meat consumption?
Gradually reducing red meat consumption can be achieved by making small changes over time. Start by substituting red meat with plant-based alternatives for one or two meals per week. Gradually increase the frequency of meatless meals and experiment with new recipes incorporating different protein sources. Planning meals in advance and gradually reducing portion sizes of red meat can also help in the transition towards a lower consumption.
Are there any potential risks of reducing red meat consumption?
Reducing red meat consumption can be beneficial for many individuals, but it is important to ensure a balanced diet to avoid potential risks. Red meat is a rich source of important nutrients such as iron, zinc, and vitamin B12. Therefore, individuals who reduce red meat intake should pay attention to obtaining these nutrients from other food sources or consider supplementation if necessary. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can help ensure a well-planned and nutrient-rich diet.



