Within the intricate realm of medical mysteries, lies a perplexing phenomenon that plagues the depths of our bodies with relentless persistence. Something that can start as a whisper, grows into a scream, heralding the arrival of a silent but formidable invader. Welcome to the enigmatic world of abscesses, where an intricate dance between our immune defenses and a cacophony of pathogenic mischief unfold.
Intriguingly clandestine, abscesses initiate their journey from hidden pockets within our bodies, shrouding their intentions beneath layers of tissue and white blood cells. These cunning infiltrators infiltrate our delicate systems through various avenues, exploiting any chance they get to wreak havoc. Whether they arise from a localized infection or present themselves as a consequence of poor oral hygiene, these pockets of chaos possess an insidious power all their own.
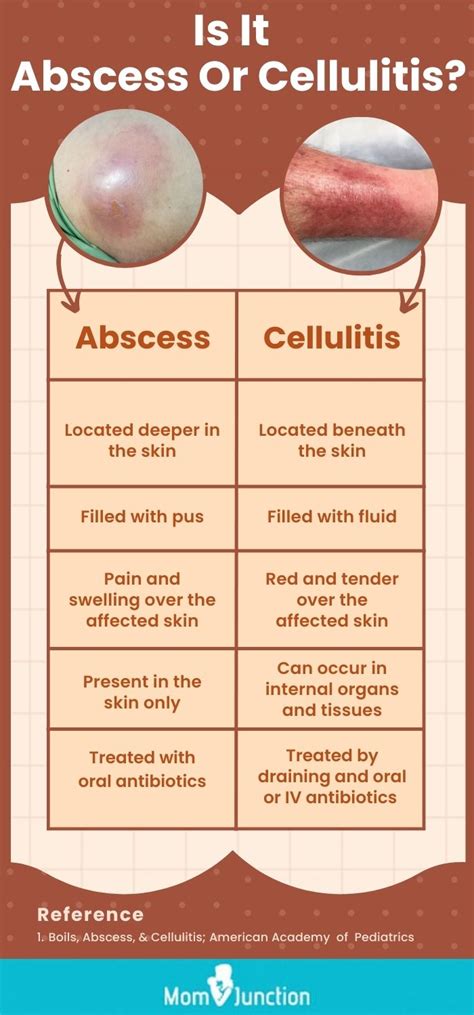
From the outside, abscesses reveal themselves through a myriad of signs and symptoms that can often be overlooked. A telltale redness, accompanied by a throbbing pain, draws attention to their presence, alerting our senses of a brewing trouble beneath the surface. And as if to assert their dominance, they often bring with them a potent accomplice - the dreaded pus. A viscous fluid loaded with microscopic combatants, pus signifies a battle of epic proportions between our body's defense mechanisms and the relentless pathogens lurking within the abscess.
When confronted with these unsettling intruders, treatments leap into action, seeking to eradicate the abscess and restore harmony within the body. Armed with an arsenal of approaches, medical professionals employ a range of interventions, depending on the severity and location of the abscess. Surgical drainage, antibiotics, and meticulous wound care dance together, playing off each other's strengths to bring an end to this silent war.
Ultimately, understanding the origin, manifestations, and resolution of abscesses shines a light on the power struggle between our bodies and the unseen forces that seek to disrupt our delicate equilibrium. By delving deep into this enigmatic realm, we gain a newfound appreciation for the resilience of our body's defense mechanisms, and the ingenuity of medical interventions designed to unmask and overcome the mysteries behind abscesses.
The Hidden Risks of Abscesses
Discover the concealed perils that can accompany abscesses as we delve into the darker aspects of this medical condition. While abscesses might appear innocuous on the surface, they harbor potential dangers that may cause distress and complications if left untreated.
The Silent Menace:
Behind the curtain of abscesses lies a hidden menace that can wreak havoc on the body. These concealed dangers can quietly infiltrate healthy tissues and spread infection, posing a significant threat to one's overall well-being. The insidious nature of abscesses magnifies the importance of promptly recognizing and addressing their presence.
Unforeseen Consequences:
As abscesses develop beneath the skin's surface, the surrounding tissues are exposed to various unforeseen consequences. The presence of an abscess can incite inflammation, causing redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area. In more severe cases, the infection can progress and lead to the formation of pus, which necessitates medical intervention to prevent further complications.
The Hidden Pathways:
A lesser-known aspect of abscesses is the potential for infection to traverse unexpected pathways within the body. These hidden routes can allow the abscess to spread beyond its initial location, potentially affecting vital organs or tissues. Vigilance is crucial, as the hidden pathways of abscesses can dramatically impact the outcomes and treatments required.
Mitigating the Risks:
Recognizing the hidden dangers of abscesses is the first step towards mitigating their risks. Seeking prompt medical attention when symptoms arise, such as localized pain, tenderness, and abnormal swelling, is imperative. Proper diagnosis, treatment, and diligent care can help curb the potential complications associated with abscesses and ensure a successful recovery.
In conclusion, abscesses may be more treacherous than initially perceived. Understanding the hidden dangers they possess is paramount to safeguarding one's health and well-being. By remaining vigilant and seeking professional medical assistance, the risks associated with abscesses can be effectively managed, leading to a more positive outcome.
Understanding the Nature of Abscesses
Achieving a deep comprehension of the essence and characteristics that define abscesses is of paramount importance. By delving into the core nature of these pathological formations, we can gain insight into their underlying causes, distinct set of signs and symptoms, as well as a range of effective treatment approaches.
1. Anatomical Insights: To understand the nature of abscesses, it is essential to explore their anatomical origins. These localized collections of pus often develop as a result of bacterial infection, which infiltrates various tissues and triggers an inflammatory response. This intruding microbial presence, combined with the body's immune defense mechanisms, culminates in the formation of an abscess.
- Microbial Intruders: Abscesses are commonly caused by diverse strains of bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. These infectious agents actively exploit vulnerabilities within the body's natural barriers, gaining access to deeper tissue layers where they can proliferate and incite abscess formation.
- Inflammatory Response: Inflammation plays a pivotal role in the development of abscesses. As the body tries to combat the invading bacteria, immune cells release various chemicals that promote blood vessel dilation and recruit additional immune cells to the infected site. This localized immune response leads to the accumulation of pus, characterized by dead cells, tissue debris, and a fluid composed of bacteria-fighting agents.
2. Symptoms and Clinical Presentation: Recognizing the key manifestations associated with abscesses is crucial for early detection and appropriate management. While the specific symptoms may vary depending on the location and severity of the abscess, there are common indicators to be aware of:
- Pain and Tenderness: Abscesses often manifest as localized pain, tenderness, and swelling. The affected area may exhibit redness and feel warm to the touch, indicating the ongoing inflammatory process.
- Fluctuance and Pus Drainage: As the abscess matures, it may grow in size, leading to the formation of a distinct pocket filled with pus. This accumulation of infectious material can cause the abscess to become more noticeable and may result in drainage of pus upon manipulation or incision.
- Fever and Systemic Symptoms: In some cases, particularly when the abscess is large or located in a deeper tissue layer, individuals may experience systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, fatigue, and an overall sense of illness.
3. Treatment Approaches: Understanding the nature of abscesses empowers healthcare professionals and patients alike to pursue effective treatment strategies. The management typically involves a combination of medicinal interventions and procedural interventions:
- Antibiotics: In cases where the abscess is small and localized, antibiotics may be prescribed to combat the underlying infection and prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Incision and Drainage: Larger abscesses often necessitate a minor surgical procedure known as incision and drainage. This technique involves making a small incision to allow for the controlled release of pus and debris, promoting faster healing and relieving pain.
- Post-treatment Care: Proper wound care, such as dressings, antibiotics, and regular follow-up visits, is vital to ensure complete resolution of the abscess and minimize the risk of recurrence or complications.
By grasping the fundamental aspects that underlie the nature of abscesses, individuals can equip themselves with the knowledge necessary to identify early warning signs, seek timely medical intervention, and facilitate a swift recovery.
The Factors Behind Abscess Formation
When it comes to the occurrence of abscesses, several factors are involved in their formation. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial in identifying and effectively treating abscesses.
Infection: One of the primary factors leading to the development of an abscess is infection. Infections can enter the body through various routes, such as cuts, wounds, or through the bloodstream. Microorganisms, like bacteria, find their way into the tissues and produce localized inflammation, resulting in the formation of an abscess.
Blockage: Another significant cause behind abscess formation is the obstruction of ducts or passageways within the body. When these pathways become blocked, it hampers the natural flow of bodily fluids, leading to a buildup of substances. The accumulation of these substances creates an ideal environment for bacterial growth and subsequent abscess formation.
Inflammation: Inflammation plays a vital role in the formation of abscesses. Chronic inflammation, often due to conditions like cysts or inflammatory bowel disease, can result in the development of abscesses over time. The ongoing inflammatory response weakens the affected tissues and promotes the growth of microorganisms, leading to abscess formation.
Weakened Immune System: A weakened immune system can also contribute to abscess formation. When the body's defense mechanisms are compromised, it becomes easier for bacteria to invade and cause infections. Immunodeficiency disorders, autoimmune conditions, or prolonged use of certain medications can all compromise the immune system, increasing the risk of abscess formation.
Foreign Bodies: In some cases, foreign bodies such as splinters, debris, or objects left inside the body after surgery can trigger the formation of an abscess. When foreign materials are present, they can serve as a breeding ground for bacteria, leading to infection and subsequent abscess development.
By understanding the various factors that contribute to abscess formation, individuals can take preventive measures and seek appropriate treatment when necessary. Prompt identification and management of these underlying causes can help minimize the risk and impact of abscesses in the body.
Identifying the Signs and Symptoms of Abscesses
Identifying the signs and symptoms of abscesses can be crucial in detecting and treating these painful and potentially dangerous infections. By recognizing the telltale signs, individuals can seek medical attention promptly and take necessary precautions to prevent further complications.
1. Localized Swelling: One of the common signs of an abscess is a localized swelling in the affected area. This swelling may be accompanied by redness and tenderness, indicating the presence of an underlying infection.
2. Pain and Discomfort: Abscesses often cause significant pain and discomfort, which can range from mild to severe. The affected area may feel tender to the touch and may be accompanied by throbbing pain or a constant dull ache.
3. Fever and Chills: In some cases, abscesses can lead to systemic symptoms such as fever and chills. These symptoms indicate that the infection may be spreading beyond the affected area and require immediate medical attention.
4. Pus or Fluid Drainage: As the abscess progresses, it may develop a fluctuant mass filled with pus or fluid. The presence of pus can be a clear indication of an abscess and may require medical intervention for proper drainage and treatment.
5. Difficulty in Movement: Depending on the location of the abscess, individuals may experience difficulty in movement due to pain or swelling. This can hamper daily activities and further emphasize the need for timely medical evaluation.
6. General Malaise: Abscesses can also cause a general sense of malaise, including fatigue, weakness, and a feeling of being unwell. These symptoms may be attributed to the body's immune response to the infection and may resolve with proper treatment.
It is important to note that these symptoms may vary depending on the location and severity of the abscess. If any of these signs or symptoms are observed, it is highly recommended to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
How Abscesses Can Impact Your Well-being
Abscesses can have a significant impact on your overall health and well-being. When these localized pockets of infection develop within your body, they can cause a range of symptoms and complications. It is important to understand the potential health consequences associated with abscesses in order to seek proper diagnosis and treatment.
1. Disrupting bodily functions: Abscesses can disrupt the normal functioning of various body systems, depending on their location. They can impair organ function, hinder blood circulation, or affect the proper drainage of fluids in the body. This disruption can lead to discomfort, pain, and functional limitations.
2. Systemic infection: If left untreated, abscesses can progress and result in a systemic infection. This occurs when the infection spreads throughout the body, affecting multiple organs and causing more severe symptoms. Systemic infections can pose a serious threat to your health and may require immediate medical attention.
3. Compromised immune response: Abscesses can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to other infections. The presence of an abscess can divert the immune system's resources and compromise its ability to defend against other pathogens. This can leave you vulnerable to secondary infections and prolonged illness.
4. Chronic pain and discomfort: Abscesses can cause persistent pain and discomfort, especially if they are large or in sensitive areas of the body. The pain can be sharp, throbbing, or constant, depending on the size and location of the abscess. This can negatively affect your quality of life and overall well-being.
5. Scarring and tissue damage: In some cases, abscesses can cause scarring and tissue damage as a result of the body's natural healing process. This can lead to long-term cosmetic concerns and functional impairments, particularly if the abscess is located in a visible or crucial area of the body.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect the presence of an abscess or are experiencing related symptoms. Proper diagnosis and treatment can help mitigate the potential health impacts of abscesses and aid in your overall recovery and well-being.
Seeking Timely Medical Treatment for Abscesses
Recognizing the importance of prompt medical attention when confronted with abscesses can significantly affect the outcome of the condition. Efficiently seeking appropriate medical treatment is essential to ensure proper management and alleviate any potential complications. This section discusses the significance of timely action and the potential benefits it can bring in the context of abscesses.
Timely medical treatment for abscesses plays a pivotal role in preventing the deterioration of symptoms and promoting effective healing. Swiftly consulting a healthcare professional allows for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis of the underlying cause, facilitating targeted treatment strategies. Timeliness in seeking medical intervention can minimize the development of more advanced symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
By promptly accessing medical care, individuals increase the likelihood of receiving timely and appropriate treatment options tailored to their unique circumstances. Medical professionals possess the expertise to determine whether conservative methods, such as antibiotics or drainage, are necessary or if surgical intervention is required to eradicate the abscess completely. Each case differs, making it crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure the most suitable course of action.
Additionally, timely medical treatment allows for effective pain management, enhancing the overall comfort and well-being of individuals with abscesses. Medical professionals can provide adequate pain relief measures to alleviate discomfort and promote a better quality of life during the healing process.
When facing abscesses, whether superficial or deep-seated, it is essential to prioritize seeking timely medical treatment. Doing so ensures proper management of the condition, minimizes complications, and enhances the likelihood of a swift recovery. Remember to consult a healthcare professional to receive personalized guidance and appropriate intervention based on your specific needs.
The Importance of Antibiotics in Treating Abscesses
When it comes to addressing the presence of abscesses, an essential component of effective treatment is the use of antibiotics. These powerful medications play a critical role in combating infection and promoting healing.
Antibiotics work by targeting the bacteria responsible for abscess formation, helping to eliminate the infection at its source. They can be administered orally or through intravenous methods, depending on the severity and location of the abscess.
In addition to directly combating bacteria, antibiotics also help to prevent the spread of infection to surrounding tissues. By eradicating the bacteria before it can spread, antibiotics aid in minimizing the potential for complications and further damage to the affected area.
- One important aspect to consider when using antibiotics in abscess treatment is the proper selection of the medication. Different types of antibiotics target specific bacteria, so it is crucial to identify the causative agent before prescribing antibiotics.
- Dosage and duration of antibiotic treatment are also essential factors to consider. Adequate dosage ensures the medication reaches therapeutic levels within the body, while the duration of treatment should be sufficient to completely eradicate the infection.
- It is important to note that antibiotics may have potential side effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or allergic reactions. Therefore, careful monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare professional are necessary during the course of antibiotic treatment for abscesses.
In summary, antibiotics play a vital role in the treatment of abscesses by targeting the bacteria responsible for infection, preventing its spread, and promoting healing. With careful consideration of the appropriate medication, dosage, and duration, antibiotics can effectively aid in resolving abscesses and preventing complications.
Surgical Options for Draining and Removing Abscesses
In this section, we will explore the various medical procedures available for the efficient drainage and removal of abscesses. Abscesses are localized collections of pus that form as a result of infection or inflammation. Treating abscesses promptly is crucial to prevent further complications and promote healing.
1. Incision and Drainage (I&D):
- One common surgical option for abscess drainage is known as incision and drainage (I&D).
- During this procedure, a medical professional makes a small incision in the abscess to allow for the evacuation of pus and debris.
- Once the abscess is drained, the wound is typically left open or packed with gauze to facilitate continued drainage and prevent re-accumulation of fluid.
2. Abscess Excision:
- In cases where the abscess is larger or unable to be sufficiently drained by I&D alone, abscess excision may be necessary.
- This procedure involves removing the entire abscess, including the surrounding damaged tissue, under sterile conditions.
- After excision, the wound is typically closed with sutures or left open, depending on the nature and extent of the abscess.
3. Percutaneous Drainage:
- For some abscesses that are difficult to access surgically, percutaneous drainage may be a suitable option.
- This minimally invasive procedure involves the insertion of a catheter or needle guided by imaging techniques.
- The catheter or needle is placed directly into the abscess cavity to facilitate drainage and may be left in place for a period of time to ensure adequate drainage.
4. Advanced Surgical Techniques:
- In more complex cases, advanced surgical techniques such as ultrasound-guided drainage or endoscopic procedures may be employed.
- These techniques allow for precise visualization and targeted drainage of abscesses in challenging locations.
- The choice of surgical option depends on the individual patient's condition, the location and size of the abscess, and the expertise of the medical team.
It is important to note that the specific surgical approach and technique will be determined by the healthcare professional based on comprehensive evaluation and the unique characteristics of each abscess.
Remember to consult with a qualified healthcare provider for a proper assessment and personalized treatment plan for abscess drainage and removal.
Preventing Abscesses and Minimizing the Risks

Avoiding abscesses and reducing the chances of their occurrence is crucial in maintaining overall health. By implementing preventive measures and being aware of the potential risks, individuals can minimize the likelihood of developing abscesses and the associated complications.
- Practice good oral hygiene: Brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing regularly, and using mouthwash can help prevent oral infections that can lead to abscesses.
- Stay vigilant about hygiene practices: Keeping the skin clean and dry, especially in areas prone to moisture, can help prevent abscesses from developing on the surface of the skin.
- Take care of wounds: Proper wound care, including cleaning and dressing wounds promptly, can prevent bacterial infections that may lead to abscess formation.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Sharing personal items such as towels, razors, or needles can increase the risk of spreading bacteria and developing abscesses.
- Be cautious with invasive procedures: When undergoing medical procedures or receiving injections, make sure proper sterilization techniques are followed to reduce the risk of abscess formation.
- Maintain a strong immune system: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can help boost immunity and reduce the risk of infections that can lead to abscesses.
- Seek timely medical attention: If any signs or symptoms of an infection or abscess develop, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications.
- Follow prescribed treatments: If diagnosed with an abscess or infection, it is essential to follow the prescribed treatments, including taking medications as directed and attending follow-up appointments.
By incorporating these preventative measures into daily life and being proactive in maintaining overall health, individuals can minimize the risk of abscess development and promote optimal well-being.
When to Seek Medical Help for Abscesses
If you are experiencing unusual symptoms or suspect that you may have an abscess, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional promptly. Seeking medical assistance is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment to prevent any complications.
While it can be tempting to self-diagnose or attempt home remedies, it is strongly recommended to consult a healthcare professional to ensure proper care. They have the knowledge and expertise to evaluate your symptoms, conduct necessary tests, and determine the appropriate course of action.
If you notice any of the following signs or symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention:
- Localized swelling, redness, and warmth
- Severe pain or tenderness around a specific area
- Pus or discharge from the affected area
- Fever and chills
- Difficulty or pain while moving or using the affected body part
- Unexplained fatigue or weakness
Additionally, if you have a weakened immune system, such as from a chronic illness or recent surgery, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional promptly if you suspect an abscess. People with conditions such as diabetes or HIV/AIDS may have a higher risk of developing abscesses and require specialized care.
Remember, early detection and appropriate treatment can help prevent the spread of infection and potential complications. Therefore, it is essential not to delay seeking medical help when experiencing symptoms that may indicate an abscess.
FAQ
What is an abscess?
An abscess is a collection of pus that forms within the body. It is usually caused by a bacterial infection and can occur in various parts of the body, including the skin, organs, or even deep within the tissues.
What are the common causes of abscess formation?
Abscesses can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacterial infections, such as staphylococcus or streptococcus, foreign substances in the body, like splinters or injections, blockage of glands or hair follicles, as well as certain medical conditions that weaken the immune system.
What are the symptoms of an abscess?
The symptoms of an abscess may vary depending on its location, but common signs include localized swelling, redness, warmth, and pain at the affected area. Other symptoms may include fever, chills, fatigue, and in some cases, the abscess may produce a discharge or fluid.
How are abscesses diagnosed?
Diagnosing an abscess usually involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. They may also perform imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or CT scan, to determine the size and location of the abscess. In some cases, a sample of the pus may be collected for laboratory analysis to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.
What are the treatment options for abscesses?
The treatment of an abscess generally involves draining the pus and treating the underlying infection. This can be done through a minor surgical procedure to open and drain the abscess, or by using a needle to withdraw the fluid. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to fight the infection. In more severe cases, the abscess may need to be surgically removed.



