In the realm of potential hazards that loom over our daily lives, there exists a peril that strikes fear in the hearts of many–a peril that emerges from the invisible realm of electricity, where death lurks silently, ready to seize its unsuspecting victims. The electric menace, with its capacity to wreak havocs on the human body and cause irreversible damage, is a phenomenon that has captivated the minds of experts and civilians alike, instilling a sense of deep trepidation and respect.
When faced with the treacherous force that underlies electric shock, one cannot help but be overcome with an intensified sense of vulnerability, as if standing at the edge of a precipice, teetering between life and an uncertain demise. The mere thought of electric current coursing through our frail bodies, disrupting the delicate balance of our existence, commands awe and terror simultaneously. It is a fear that is universally shared, transcending borders and cultures, highlighting the primal instinct of self-preservation ingrained within us.
The enigmatic nature of electric shock, coupled with the unpredictability of its consequences, amplifies our unease and fuels our apprehensions. Encountering this formidable threat unveils the fragility of human life and forces us to confront our own mortality. It is in these moments of realization that we come face to face with the haunting possibility of being stripped away from our loved ones and the familiar world we call home.
Cracking the code of this fear requires not only a comprehensive understanding of the science behind electric shock, but also an acknowledgment of its psychological impact on individuals. It demands a journey into the inner sanctum of our minds, where the fear of the unknown intertwines with the fear of losing control. By venturing into this realm of knowledge, we can hope to shed light on the darkness that engulfs our thoughts and ultimately find solace in the power of awareness and precaution.
The Silent Killer: Unraveling the Electrical Safety Myth

Often underestimated and misunderstood, the discreet danger lurking within our electrical systems has been given the name "The Silent Killer". This captivating moniker refers to the widely disseminated myth that electricity is safe as long as we follow basic precautions. However, beneath the surface lies a world of potential hazards that demands our attention and understanding.
Challenging popular misconceptions, this section aims to unravel the prevailing electrical safety myth by delving into the various risks associated with electricity. Through exploring real-life incidents, insightful data, and expert analysis, we will shed light on the true nature of this silent killer, debunking the notion that electrical safety is a trivial matter.
By acknowledging the lesser-known dangers that exist within our daily lives, our understanding of electrical safety will be heightened. This newfound knowledge will empower individuals to take necessary precautions, and equip them with the tools to mitigate risks effectively. Together, we can work towards ensuring a safer and more informed community, free from the grip of "The Silent Killer".
An Unfortunate Combination: The Lethality of Voltage and Current
When it comes to the perils of electrical accidents, it is crucial to understand the deadly combination posed by both voltage and current. This article aims to shed light on the inherent dangers of this lethal pairing, exploring the intricacies of how they contribute to the potentially fatal consequences of electric shock.
Electric shock, stemming from exposure to high voltage and current, can have dire consequences for the human body. It is imperative to recognize that voltage refers to the electrical potential difference between two points, while current is the flow of electric charge. While voltage alone can be dangerous, it is the synergistic effect of voltage and current that poses the greatest threat to human life.
Voltage, often described as the "push" behind electric current, determines how strongly electricity flows through a circuit. When exposed to excessive voltage, the body becomes an unwitting conductor, as the path of least resistance for the electrical current. This can lead to a multitude of physiological effects, ranging from mild tingling sensations to severe burns, internal injuries, and even cardiac arrest.
Current, the actual flow of electric charge, determines the intensity and severity of the electric shock. Higher current levels can significantly increase the risk of tissue damage and the subsequent impairment of vital organs. The human body, predominantly composed of water, serves as an excellent conductor for electric current, making it particularly vulnerable to the dangers posed by excessive electrical flow.
The physiological impacts of electric shock are immensely varied and can affect several systems in the body. The nervous system, in particular, is intricately linked to the passage of electric current. Severe shocks can disrupt the proper functioning of the nervous system, potentially resulting in muscle spasms, respiratory distress, and even paralysis.
In conclusion, comprehending the lethal union of voltage and current is essential for understanding the gravity of electric shock accidents. By recognizing the potential harm they can cause, individuals can take the necessary precautions to safeguard themselves against the dangers of electric shock and ultimately mitigate the risk of its deadly consequences.
Overcoming the Fear: Clearing Misconceptions about Electrical Accidents

In this section, we will explore common misconceptions surrounding incidents involving electrical current and address important facts that can help dispel fear and anxiety.
- Electricity: Separating Myth from Reality
- Understanding the True Risks Involved
- Debunking Popular Beliefs about Electric Shock
- Knowing the Difference: Low Voltage vs. High Voltage
- Electrical Safety Measures: The Importance of Education and Training
- Breaking the Stereotypes: Examples of Survivors
- Building Confidence: Expert Advice on Preventing Electrical Accidents
By addressing these misconceptions, gaining a better understanding of the actual risks, and learning from real-life cases of survival, we can help individuals overcome their fear of electric shock and develop a more informed approach to electrical safety.
The Impact of Electric Shock on Human Health
When an individual comes into contact with an electrical current, it can have significant consequences for their well-being. Understanding the effects of electric shock on the human body is crucial for raising awareness and promoting safety measures.
Physical Consequences: Electric shock can have a wide range of physical effects on the human body. In some cases, it may lead to burns, muscle contractions, or even cardiac arrest. The severity of these consequences depends on several factors, including the voltage of the electrical current and the duration of exposure. Repeated exposure to electric shock can also result in long-term physiological damage.
Neurological Impact: Electric shock can have a profound impact on the nervous system. It can disrupt the normal functioning of nerve cells, leading to nerve damage, pain, and even the loss of sensation or motor control in certain body parts. The extent of the neurological consequences can vary depending on the intensity of the electric shock and the pathways affected within the nervous system.
Psychological Effects: Electric shock incidents can also have psychological repercussions. Survivors may experience symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, or depression as a result of the traumatic event. The fear and anxiety associated with the possibility of being exposed to electric shock again can also greatly impact an individual's mental well-being.
Long-Term Health Implications: Electric shock incidents can result in long-term health complications. These may include chronic pain, cognitive difficulties, and an increased risk of developing cardiovascular or neurological disorders. Additionally, individuals who have experienced electric shock may face challenges in their daily lives, such as difficulties with mobility or engaging in certain activities.
In conclusion, it is essential to understand the various effects of electric shock on human health. By doing so, we can work towards implementing preventative measures and promoting safety practices to minimize the risks associated with electrical accidents.
The Astonishing Figures: Exploring the Global Occurrence of Fatal Electrical Accidents
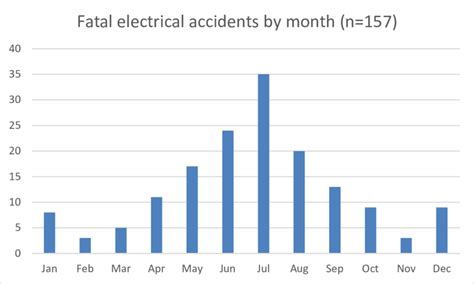
While the mere thought of encountering an electric shock can send shivers down anyone's spine, the reality is that such incidents are not as rare as one might imagine. Around the world, fatal accidents caused by electrical shocks claim numerous lives each year, leaving behind a trail of devastation and sorrow. This section delves into the shocking statistics surrounding electric shock deaths, shedding light on the widespread impact of these tragic incidents.
- Epidemic of Tragedy: An in-depth analysis reveals that electrical accidents resulting in fatalities occur at an alarming rate across various regions, transcending geographical borders.
- Global Variances: While some countries witness a higher incidence of electric shock deaths due to inadequate safety regulations and substandard infrastructure, others have managed to implement strict measures and significantly reduce such incidents.
- Vulnerable Population: Among the victims of electric shock fatalities, a significant percentage comprises individuals working in hazardous occupations like construction, engineering, electrical installation, and maintenance.
- Age and Gender Patterns: Studies indicate that certain age groups and genders are more prone to electric shock deaths, emphasizing the need for targeted awareness campaigns and safety measures.
- Underreported Cases: Unfortunately, the actual number of electric shock fatalities may be higher than official records suggest, as numerous incidents go unreported or are misclassified due to various factors.
The aim of examining the global incidence of electric shock deaths is not to incite fear but to raise awareness about the gravity of such incidents and the urgent need for enhanced safety standards worldwide. By understanding the alarming statistics surrounding electric shock fatalities, we can work towards preventing future tragedies and safeguarding human lives.
Preventing Accidents: Essential Safety Measures for Electrical Equipment
In order to ensure the well-being of individuals and avoid potentially life-threatening situations, it is crucial to prioritize prevention when it comes to using electrical equipment. By implementing a set of essential safety measures, we can significantly reduce the risks associated with electric shock and promote a safe working and living environment.
| Safety Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Inspections | Periodically inspect all electrical equipment to identify potential hazards or signs of deterioration. This will help detect and prevent any potentially dangerous situations. |
| Proper Installation | Ensure that all electrical equipment is correctly installed by trained professionals to minimize the likelihood of faulty connections or insufficient grounding. |
| Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) | Install GFCIs in areas where electrical equipment is used in close proximity to water sources, such as bathrooms and kitchens. GFCIs will automatically shut off the power if there is a ground fault, reducing the risk of electric shock. |
| Adequate Training | Provide comprehensive training to individuals who are responsible for operating or maintaining electrical equipment. It is essential that they understand the correct procedures and safety protocols to follow. |
| Regular Maintenance | Establish a routine maintenance schedule to ensure that all electrical equipment is kept in good working condition. This includes cleaning, lubricating, and replacing any worn-out parts. |
| Safe Work Practices | Enforce proper work practices, such as using insulated gloves and tools, turning off equipment before performing maintenance or repairs, and avoiding shortcuts that may compromise safety. |
| Proper Labeling | Clearly label all electrical equipment to indicate their voltage requirements, potential hazards, and safety instructions. This will help individuals handle the equipment correctly and reduce the risk of accidents. |
By implementing these essential safety measures, individuals can significantly mitigate the risk of electric shock incidents and promote a safer environment for all. It is vital to prioritize prevention by staying vigilant, conducting regular inspections, and ensuring that all safety protocols are followed when dealing with electrical equipment.
Securing Your Home: Shielding Kids from Electrical Accidents

Ensuring the safety of young ones within a domestic environment necessitates careful attention to potential hazards related to electricity. This section offers essential guidance on childproofing your home, reducing the risk of electrical accidents, and implementing preventive measures to safeguard children from coming into contact with electrical dangers.
1. Covering Outlets
One crucial step to prevent electric shocks involves covering all accessible electrical outlets. Utilize childproof outlet covers or safety plugs to block these openings. This simple yet effective measure significantly diminishes the likelihood of children inserting objects into outlets, minimizing the risk of electrical shock incidents.
2. Securing Cords and Wires
Properly managing cords and wires is central to safeguarding children from electrical accidents. Secure loose cords by using cord covers or organizing them out of reach. Furthermore, avoiding the use of extension cords and ensuring adequate grounding of all electrical appliances significantly reduces the potential for electrical shock hazards.
3. Restricting Access to Electrical Devices
To prevent tampering with electrical devices and potential electric shock accidents, it is crucial to restrict access to them. Place childproof locks on cabinets and drawers that contain appliances and electrical equipment. Additionally, consider mounting TVs and other large electronics securely to prevent them from toppling over and causing harm.
4. Adequate Lighting
Improving lighting conditions throughout the home can minimize the risk of electric shock accidents. Enhancing visibility not only helps children navigate their surroundings safely but also enables them to identify potential electrical hazards more easily. Install sufficient lighting fixtures, especially in areas where electrical panels, outlets, and electrical wires are located.
5. Educating and Supervising
Teaching children about electrical safety and supervising their activities around electrical devices are crucial aspects of childproofing your home. Educate them on the potential dangers of electricity and explain the importance of following safety rules. Regularly supervise children's interactions with electrical appliances and emphasize the need to alert an adult if they encounter any electrical hazards.
By implementing comprehensive childproofing measures and ensuring a supervised environment, parents and caregivers can effectively protect children from electric shock hazards within their home. Prioritizing electrical safety enhances the overall well-being and reduces the risk of accidents, providing families with peace of mind.
On the Job: Occupational Hazards and Safety Guidelines for Workers
When it comes to working in various industries, employees are often exposed to certain risks and dangers associated with their occupation. In order to ensure their safety and well-being, it is crucial for both employers and workers to be aware of these occupational hazards and to follow established safety guidelines.
- 1. Identifying Potential Hazards
- 2. Training and Education
- 3. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- 4. Regular Inspections and Maintenance
- 5. Emergency Preparedness
- 6. Reporting and Communication
- 7. Ongoing Safety Oversight
One of the first steps in addressing occupational hazards is to identify and understand the potential dangers within a specific work environment. This includes recognizing equipment malfunctions, faulty wiring, and unsafe procedures that could lead to accidents or injuries.
Employers should provide comprehensive training and education programs to inform workers about the potential hazards they may encounter on the job. This includes teaching proper handling techniques, emergency response procedures, and the use of appropriate safety equipment.
Workers should be provided with the necessary personal protective equipment, such as safety helmets, goggles, gloves, and earplugs, to minimize the risk of injury or exposure to hazardous substances. It is essential for employees to utilize PPE consistently and correctly.
Regular inspections and maintenance of equipment and machinery are crucial for identifying potential hazards and addressing any malfunctions or defects promptly. Employers should establish routine maintenance schedules and encourage workers to report any issues they observe.
Having a well-defined emergency preparedness plan is essential for mitigating the effects of potential accidents or hazardous situations. This includes providing clear instructions on emergency evacuation procedures, identifying emergency exits, and conducting regular drills to ensure workers are familiar with the correct response protocols.
A culture of open communication and reporting is vital to maintaining a safe work environment. Workers should feel comfortable reporting hazards, near misses, or unsafe conditions to their supervisors or safety officers promptly. Regular safety meetings and discussions can also enhance awareness and prevent potential incidents.
Safety guidelines and protocols should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect any changes in the work environment or industry standards. Employers should conduct periodic safety audits, involve employees in the decision-making process, and encourage ongoing training and awareness.
By prioritizing occupational safety, employers can protect their workers from potential hazards and create an environment where employees can carry out their duties without fear of unnecessary accidents or injuries. Likewise, workers should remain vigilant, adhere to safety guidelines, and report any hazards or concerns to ensure a safer and healthier workplace for all.
First Aid for Electric Shock: Knowing How to Respond in an Emergency

In situations where individuals are exposed to the hazards of electrical current, it is crucial to be prepared and aware of the appropriate first aid measures. Understanding how to respond effectively during an electric shock emergency can make a significant difference in potentially saving lives. This section provides essential guidelines on what actions to take when faced with such an incident, emphasizing the importance of quick and informed reactions.
1. Ensure Personal Safety
Prioritize personal safety by turning off the electrical source or interrupting the current flow, if possible, before physically approaching the individual. It is important to avoid direct physical contact with the person experiencing electric shock to prevent oneself from becoming a secondary victim. Remember to assess the surroundings for any further potential dangers, such as wet or conductive surfaces.
2. Call for Help
Contact emergency medical services immediately (e.g., dialing emergency services with the respective local number) to ensure professional assistance is on the way. Provide accurate and concise information about the situation, including the location and the individual's condition, to aid in the prompt response of the emergency services.
3. Safely Disconnect the Electric Source
If it is safe to do so, turn off the power source or unplug the affected equipment using insulated gloves, non-conductive materials, or a dry wooden object. Avoid using water or any conductive material to avoid worsening the situation. Only take action if you are certain it is safe to do so, ensuring your own safety first.
4. Assess the Individual
Once the electrical source is disconnected, assess the person who has been electrocuted cautiously. Check for signs of consciousness, breathing, and circulation. If the person is not breathing or their heart has stopped, promptly begin CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) until professional help arrives. Avoid moving the individual unless there is an immediate danger present.
5. Do Not Apply Direct Contact
Avoid touching the person while providing help to minimize the risk of receiving an electric shock yourself. Using non-conductive materials, such as a dry cloth or towel, to create a barrier between yourself and the individual, can allow safer assistance without direct contact.
6. Wait for Medical Professionals
Continue to monitor the person's condition and provide reassurance until medical professionals arrive. Avoid leaving the individual unattended and be prepared to provide further information regarding the incident to the medical responders.
By following these guidelines, individuals can ensure that they provide the necessary first aid support during an electric shock emergency. Remember, quick and informed actions can make a vital difference in preventing severe consequences and saving lives.
FAQ
What are the dangers of electric shock?
Electric shock can lead to severe injuries, including burns, nerve damage, muscle contractions, and even death. Additionally, it may cause cardiac arrest, respiratory failure, or other life-threatening complications.
How does electric shock occur?
Electric shock occurs when a person comes into contact with an electric current. This can happen through direct contact with a live wire, faulty electrical appliances, or by being exposed to water or conductive surfaces that have an electrical current running through them.
What are the symptoms of electric shock?
The symptoms of electric shock can vary depending on the severity of the incident. They may include burns, numbness or tingling, difficulty breathing, muscle pain or contractions, seizures, and loss of consciousness.
Why do people have a fear of being electrocuted to death?
People may have a fear of being electrocuted to death due to the severe consequences that electric shock can have on the body. The possibility of injury or death, along with the pain and suffering associated with electric shock, can create a deep-rooted fear in individuals.
How can one protect themselves from electric shock?
To protect oneself from electric shock, it is important to ensure that electrical appliances are properly maintained and grounded. Avoid contact with live wires and always use insulated tools when working with electricity. It is also crucial to keep water away from electrical devices and outlets and to familiarize oneself with basic electrical safety measures.
What are the potential dangers of electric shock?
Electric shock can lead to a range of injuries, from mild burns to cardiac arrest or death. The severity of the injuries depends on the amount of electric current, the path the current takes through the body, and the duration of exposure. It can cause muscle contractions, respiratory distress, thermal burns, and damage to internal organs. In certain cases, it can also lead to psychological trauma or long-term neurological complications.



