Imagine a world where the once-firm grip of the global petroleum industry starts to loosen. A realm where the price tags of vital energy resources plummet to unprecedented lows, ushering in an era of economic transformation and environmental opportunity. In this narrative, the world envisions a future where the cost of crude oil, a pivotal catalyst for modern development, dramatically diminishes, altering the very fabric of our existence.
Fantasize about an alternative timeline where the value of fossil fuels experiences a seismic shift downwards, allowing individuals, industries, and nations alike to witness a surreal reconfiguration of their financial landscapes. Substantial savings and an enhanced disposable income for individuals, coupled with enhanced competitiveness and profitability for businesses, become the hallmark of this transformative moment in history. Industries no longer tethered by exorbitant energy costs explore new realms of innovation and efficiency, while consumers revel in the financial relief offered by alternative and renewable energy sources.
Envision a global scenario where escalating concerns over greenhouse gas emissions and climate change find solace in the form of mercifully low energy prices. With reduced reliance on traditional fuels, nations now march steadfastly towards carbon neutrality, undertaking ambitious projects to harness the power of renewable energy. This newfound affordability empowers governments, corporations, and individuals to devote substantial resources towards the implementation of sustainable practices and green technologies, ensuring a brighter and cleaner future for generations to come.
The Impact of Fluctuating Energy Costs on Global Economy
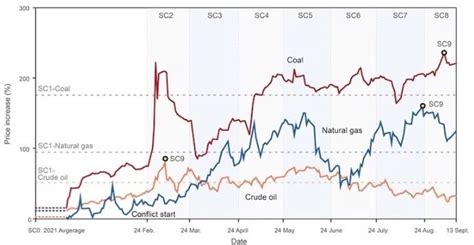
Energy prices play a crucial role in shaping the global economy, influencing various sectors and impacting nations worldwide. The fluctuation in energy costs, particularly in the oil industry, holds immense significance in determining economic stability, trade dynamics, and geopolitical relationships. In this section, we will delve into the profound effects that the rise and fall of energy prices have on the global economy.
Economic Performance: The volatility of energy prices exerts a significant influence on the overall economic performance of countries. When energy costs soar, businesses experience increased production expenses, causing a ripple effect on consumer prices and inflation rates. Higher fuel prices also burden transportation and logistics, raising the costs of goods and services. On the other hand, declining energy prices can provide relief to industries, allowing for higher profit margins, increased investments, and improved consumer spending.
Trade Balance: Energy is an essential component of international trade, with oil being a key commodity. A steep increase in oil prices can lead to trade imbalances for countries that rely heavily on imports, as energy expenditure rises. Consequently, nations dependent on oil exports benefit from surging prices, witnessing trade surpluses and potential economic growth. Conversely, declining oil prices equate to reduced import costs, alleviating the pressure on trade deficits and impacting the trade balance in favor of oil-importing nations.
Geopolitics: Energy prices and geopolitical dynamics are intrinsically intertwined. Countries possessing significant oil reserves leverage their resources as geopolitical tools, often shaping alliances and rivalries. An increase in prices can bolster the economies of oil-producing nations and grant them greater political influence on the global stage. However, a decline in oil prices weakens their leverage, straining their ability to wield influence and potentially reshuffling the geopolitical landscape.
Investment and Innovation: Fluctuating energy prices can have a profound impact on investment patterns and innovation within various industries. High oil prices incentivize exploration and production activities, encouraging investments in renewable energy sources and technological advancements. Conversely, lower fuel costs may divert investments away from renewable sources and hinder progress toward sustainable energy alternatives. Therefore, keeping energy prices stable and predictable becomes crucial for promoting long-term investments and fostering innovation.
In conclusion, the rise and fall of energy costs, particularly in the oil industry, have far-reaching implications on the global economy. From economic performance to trade balances, geopolitics, and investments, energy prices act as a fulcrum, defining the fortunes of nations and industries alike. Understanding and adapting to these fluctuations is paramount for governments, businesses, and individuals seeking to navigate and thrive in an ever-changing economic landscape.
Changing Dynamics of International Trade
The current global economic landscape is experiencing a significant transformation in the way international trade is conducted. This shift is not only driven by the undulating fluctuations in the price of crude oil, but also by a myriad of interconnected factors that impact various industries and economies worldwide.
The evolving dynamics of international trade illustrate a changing paradigm in the global marketplace. Traditional trade patterns, once dominated by oil-dependent economies, are now being reshaped by emerging industries and alternative sources of energy. As the world diversifies its energy mix and embraces renewable resources, the dependency on oil as a key driver of commerce has begun to wane.
This transition has far-reaching implications for countries heavily reliant on oil exports. These nations are being compelled to evaluate and diversify their economic foundations, seeking new avenues of growth and development beyond traditional oil-centric sectors. The diversification of industries, such as technology, renewable energy, and manufacturing, presents opportunities for countries to adapt and thrive in this changing landscape of international trade.
Moreover, the changing dynamics of international trade also impact the overall geopolitical balance. As the traditional oil-focused economies lose their dominant positions, emerging economies that excel in other sectors rise to prominence. This shift not only alters the power dynamics among nations but also fosters collaborations and partnerships that encourage technology transfer and knowledge sharing.
In conclusion, the dream of declining oil prices has resulted in a profound transformation in the dynamics of international trade. This shift has initiated a domino effect, triggering the need for economic diversification, altering geopolitical landscapes, and creating opportunities for emerging industries. As nations navigate this changing terrain, the future of international trade holds both challenges and potential for growth and innovation.
Implications for Petroleum-Producing Nations
The impact of diminishing costs of the vital natural resource has far-reaching consequences for countries heavily reliant on petroleum exports. The changing dynamics of oil values have the potential to shape the economies, social structures, and geopolitical landscape of these nations.
As oil proceeds to exhibit a steady descent in value, nations heavily dependent on this commodity must grapple with the impending challenges and adjustments brought about by this paradigm shift. Reduced oil prices prompt these countries to reevaluate their economic strategies and diversify their income sources beyond oil revenues.
In economic terms, dwindling oil prices exert downward pressure on government budgets, necessitating cuts in public expenditure, and leading to potential financial deficits. It becomes increasingly necessary for oil-producing nations to adopt comprehensive fiscal frameworks that involve reducing dependence on oil revenues, enhancing tax systems, and diversifying into new sectors such as renewable energy or technological innovation.
Furthermore, fluctuating oil prices can disrupt social systems within these petroleum-heavy economies. The welfare and standard of living for citizens are often deeply interconnected with government revenues generated from oil exports. Therefore, diminishing oil prices can lead to reduced public services, social programs, and infrastructure investments, potentially impacting the quality of education, healthcare, and basic amenities. As a byproduct, social unrest, inequality, and political instability might surface in these regions.
Geopolitically, declining oil prices can also reshape global power dynamics and influence international relations. Nations with burgeoning petroleum production capabilities may leverage their lower production costs to gain a competitive advantage in the market, impacting the market share and influence traditionally held by established oil-producing nations. This shift can initiate geopolitical challenges and rivalries as dominant players strive to maintain control and influence over global oil supplies.
In summary, the decreasing trend in oil prices presents a wide range of implications for oil-producing nations, affecting their economic stability, social fabric, and geopolitical standing. Adapting to this new reality by implementing strategic diversification measures and sustainable economic policies will be crucial for the long-term prosperity and resilience of these countries.
Opportunities and Challenges for Consumer Countries
In the pursuit of reducing dependence on a certain natural resource, consumer countries around the world face numerous opportunities and challenges. These nations, heavily reliant on the availability and affordability of a particular fuel source, must navigate the changing dynamics of the global energy market, explore alternative energy options, and address the implications of declining resources.
Exploring Energy Diversification: The declining availability of this vital resource presents an opportunity to explore and invest in alternative energy sources. Consumer countries can prioritize research and development efforts in renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. By diversifying their energy portfolios, these nations can reduce their vulnerability to price fluctuations and potential shortages.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency: Another avenue for consumer countries to address the challenges posed by declining resources is to focus on energy efficiency measures. Improving the energy efficiency of industries, transportation systems, and residential buildings can help to reduce overall energy consumption, thereby mitigating the impact of dwindling resources. It can also lead to cost savings for consumers and contribute to environmental sustainability.
Collaboration and Regional Partnerships: Consumer countries can also seek opportunities for collaboration and partnerships with other nations, both regionally and globally. By joining hands, countries can pool their resources and expertise to develop collective strategies for addressing the challenges posed by declining resources. This can include sharing best practices, technology transfer, and establishing joint research and development projects to accelerate progress towards a sustainable and diversified energy future.
Economic Transformations: The transition away from a reliance on a specific fuel source necessitates economic transformations in consumer countries. These nations must anticipate and manage the potential socioeconomic impacts of declining oil resources. Opportunities for job creation and economic development can be found in the growth of new industries and sectors supported by the shift towards cleaner and renewable energy options.
Environmental Considerations: Lastly, consumer countries must confront the environmental considerations associated with the production and consumption of traditional energy sources. The decline in oil resources provides an opportunity to address issues related to greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and climate change. By embracing cleaner energy alternatives, consumer countries can contribute to a more sustainable future and safeguard the health and well-being of both their population and the planet.
Overall, consumer countries facing the dream of declining oil prices are presented with manifold opportunities and challenges. Through energy diversification, enhanced efficiency, collaboration, economic transformations, and environmental considerations, these nations can pave the way towards a brighter and sustainable energy future.
FAQ
What is the dream of declining oil prices?
The dream of declining oil prices refers to the hope or desire for a significant decrease in the cost of oil in the global market. This dream is often fueled by the potential economic benefits that lower oil prices can bring, such as reduced transportation costs, lower production costs for businesses, and increased disposable income for consumers.
Why do people dream of declining oil prices?
People dream of declining oil prices because it can have a positive impact on their personal finances and the overall economy. Lower oil prices can lead to lower fuel costs, making transportation and travel more affordable. Additionally, industries that heavily rely on oil, such as manufacturing and agriculture, can benefit from lower production costs. Overall, declining oil prices can stimulate economic growth and provide financial relief for individuals and businesses.
What are the potential advantages of declining oil prices?
There are several potential advantages of declining oil prices. Firstly, it can lead to lower fuel costs, reducing expenses for individuals and businesses. Secondly, industries that rely on oil as a raw material can benefit from lower production costs, which can translate into more affordable products for consumers. Additionally, lower oil prices can stimulate economic growth by increasing consumer spending power and attracting investments in other sectors. Finally, declining oil prices can also contribute to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions as cheaper oil may discourage the use of alternative, more environmentally harmful energy sources.
Are there any drawbacks to declining oil prices?
While declining oil prices can be advantageous in many ways, there are also some drawbacks to consider. Firstly, countries heavily dependent on oil exports may experience economic challenges, as their revenue from oil sales decreases. This can lead to budget deficits, unemployment, and social instability in these nations. Additionally, lower oil prices can discourage investments in renewable energy sources and alternative technologies, as the immediate cost benefits of oil outweigh the long-term benefits of sustainable energy. Finally, declining oil prices can also contribute to greater reliance on fossil fuels, which can have negative environmental consequences.
How can declining oil prices affect the global economy?
Declining oil prices can have various impacts on the global economy. Firstly, it can lead to increased consumer spending power by reducing the cost of transportation and goods. This can stimulate economic growth and boost industries that rely on consumer demand. Secondly, countries that import a significant amount of oil can benefit from lower import bills and a decrease in their trade deficit. However, oil-exporting nations may face economic challenges, as their revenue decreases. The overall effect on the global economy will depend on factors such as the balance of oil importing and exporting countries and the adaptability of industries to changing oil prices.



