When we think of communication, our minds often jump to human-to-human interactions. We imagine conversations filled with words, gestures, and expressions, as we use language to convey our thoughts and emotions. However, what if I told you that communication goes beyond the realm of humans? What if I told you that in the animal kingdom, a secret language exists, hidden beneath the surface?
For centuries, scientists and animal enthusiasts alike have been captivated by the elusive world of animal communication. Just like humans, animals have their own unique ways of expressing themselves. From the majestic roar of a lion to the haunting call of a wolf, these sounds hold meanings that we are only just beginning to unravel.
What makes animal communication so enthralling is its diversity and complexity. Unlike human communication which primarily relies on verbal language, animals communicate through a multitude of channels. They use visual displays, tactile signals, chemical cues, and even electrical impulses to convey messages to their counterparts.
While we may not fully comprehend the intricacies of animal communication, one thing is clear: it is a crucial component of their survival and social structure. Whether it's a warning signal, a mating call, or a display of dominance, these messages allow animals to navigate their environments and ensure the continuation of their species.
Diving into the Mysterious Realm of Creature Interaction

Embarking on an exhilarating journey into the enigmatic world of creature communication unveils a universe brimming with astonishing connections and invisible dialogues. Through intricate signals and intricate behavioral patterns, animals unearth the secrets of their language, inviting us to unravel the intricacies of their exquisite vernacular.
Within the realm of fauna, a multitude of species have developed fascinating mechanisms to express their emotions, intentions, and needs. By understanding the nuances of their non-verbal language and deciphering the subtleties of their communication systems, we gain invaluable insights into the mysterious realm of creature interaction.
Redefining the Paradigm of Linguistic Expression
Human communication has traditionally been considered the pinnacle of linguistic expression. However, delving into the intriguing world of animal communication exposes us to the astounding diversity and dexterity exhibited by creatures across the globe. From intricate visual displays to elaborate auditory calls, animals deploy an array of specialized techniques in order to convey their intentions and navigate the intricacies of their social groups.
The Symphony of Nature's Whispers
Nature's tapestry unfurls with a symphony of whispers, as animals expertly tune into the subtlest of cues to decipher messages emanating from their surroundings. By observing and analyzing these exchanges, humans can gain a deeper comprehension of the complex web of relationships that exists within the natural world.
Unlocking the Code of Animal Language
Revealing the intricate code of animal language presents an ongoing challenge. Researchers employ a variety of methods, including decoding vocalizations, tracking body language, and analyzing chemical signals, to uncover the deep-rooted mysteries that lie within the animal kingdom's linguistic repertoire. Through these efforts, a veil is lifted, shedding light on the remarkable complexity and intelligence that underlies the seemingly simplistic utterances of creatures that inhabit our planet.
Exploring the Various Forms of Animal Vocalization
Delving into the diverse world of animal communication unveils a remarkable array of vocal expressions that enable different species to convey messages and interact with one another. From haunting howls to melodic bird songs, the animal kingdom brims with a symphony of sounds that serve various purposes.
1. Oral Communication:
- Mammals employ a wide range of vocalizations, such as roars, growls, and chirps, to communicate effectively within their social groups.
- Birds, known for their enchanting melodies and calls, utilize their vocal cords to attract mates, defend territories, and convey warnings of potential danger.
- Reptiles and amphibians employ unique sounds, including hisses, croaks, and serenades, to communicate both within their species and across their habitats.
2. Visual Communication:
- Many animals rely on visual cues, such as body language, facial expressions, and coloration, to convey messages or establish dominance within their social hierarchies.
- Gestures and postures enable primates to communicate complex meanings and emotions within their troops or family groups.
- Insects, with their intricate mating dances, utilize visual displays to signal their availability and court potential mates.
3. Chemical Communication:
- Some animals use chemical signals, known as pheromones, to communicate with others of their species. These chemical messengers play a crucial role in marking territories, attracting mates, and signaling danger.
- Ants, for example, leave pheromone trails to guide their fellow workers to food sources, while bees employ pheromones to coordinate activities within their colonies.
- Marine mammals, such as whales, emit distinct odors to communicate with others over vast distances, allowing them to locate potential mates or identify members of their pods.
4. Echolocation and Vibrational Communication:
- Bats and dolphins use echolocation to navigate their surroundings and locate prey or obstacles using sound waves and their echoes.
- Elephants communicate through infrasound, producing low-frequency vocalizations that can travel several miles, enabling their messages to reach distant members of their herd.
- Invertebrates, like bees and ants, communicate through vibrational signals, often produced by specialized body parts, which transmit messages to other members of their colonies.
As our understanding of animal communication deepens, the intricate web of vocalizations, visual cues, chemical signals, and unique adaptations continues to astonish and captivate researchers seeking to unravel the secrets of this enigmatic world.
The Significance of Non-Verbal Cues in Decoding Interspecies Interaction
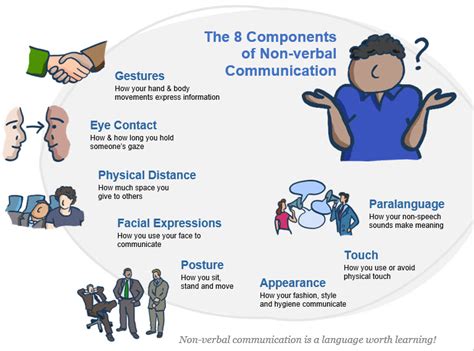
In the realm of deciphering the enigmatic language of animals, it is not only their vocalizations that hold the key to understanding their communication. Body language, an often overlooked form of non-verbal communication, plays a vital role in unraveling the intricate codes that animals use to convey their messages.
When attempting to comprehend the nuances of interspecies interaction, it becomes evident that animals deploy a wide range of non-verbal cues to express their intentions, emotions, and needs. These cues encompass a diverse array of movements, postures, and gestures that can offer deep insights into their social dynamics and intentions.
The power of body language lies in its ability to transcend linguistic barriers, enabling communication between different species. By carefully observing an animal's stance, facial expressions, and tail movements, skilled observers can gain deep insights into their motivations and feelings. For example, a swaying tail may indicate a mixture of curiosity and caution, while a lowered head and dilated pupils may signal submission or fear.
Furthermore, body language serves as a vital tool for animals to navigate their complex social hierarchies. Dominance and aggression can often be conveyed through displays of erect postures, raised fur, or bared teeth, while submissive individuals may resort to submissive gestures such as crouching or rolling onto their backs. By understanding these expressions, researchers and animal enthusiasts can gain a deeper comprehension of how social dynamics shape communication patterns within species.
Decoding the intricate web of body language in animal communication holds profound implications for various fields of study. Conservation efforts can be enhanced by understanding the signals animals use to establish territories and communicate threats. Furthermore, interventions in animal behavior and training can be made more effective and humane by taking into account non-verbal cues.
In conclusion, the study of animal communication extends beyond the confines of vocalizations and embraces body language as an essential component. By recognizing the significance of non-verbal cues in deciphering interspecies interaction, we can unlock a deeper understanding of the rich and diverse tapestry of communication present in the animal kingdom.
Unveiling the mysteries of animal vocalizations
Exploring the enigmatic world of animal vocalizations brings us closer to unraveling the hidden intricacies of interspecies communication. These distinctive sounds emitted by creatures of the wild serve as a gateway to understanding their behavioral patterns, social structures, and emotions.
The Language of Nature: Just as humans communicate through spoken language, animals possess their own unique vocal repertoire. From the melodic bird songs that grace the dawn chorus to the thunderous roars of lions echoing across the savannah, each vocalization holds meaning and purpose within the context of animal society.
Emotional Expressions: Animal vocalizations not only serve as a means of conveying information but also as a window into their emotional world. The roars of a dominant male expressing strength and dominance, the gentle purring of a contented feline, or the distress calls of a wounded animal seeking help - each vocalization provides a glimpse into the complex emotional lives of animals.
Communication for Survival: Animal vocalizations play a crucial role in survival. Rhythmic chirps alerting others to the presence of predators, intricate mating calls to attract a potential partner, or the harmonious songs of humpback whales coordinating their migratory routes - these vocalizations are essential tools that aid animals in navigating their intricate natural environments.
The Power of Observation: By carefully studying the acoustic patterns, frequencies, and variations in animal vocalizations, researchers can decipher the meaning behind each unique sound. Through scientific advancements and technological tools, we are gradually piecing together the puzzle of how animals communicate with one another.
The Beauty of Interconnectedness: Exploring animal vocalizations not only unravels the mysteries of their communication but also highlights the interconnectedness of all living beings on Earth. By gaining a deeper understanding of animals' vocal expressions, we can foster greater empathy, appreciation, and conservation efforts for the diverse array of species that share our planet.
FAQ
Why is animal communication considered important?
Animal communication is considered important because it helps researchers understand how animals interact with each other and their environment. It provides insights into their social structures, mating behaviors, and even potential threats. Additionally, studying animal communication can also help us develop a better understanding of our own communication abilities.
How do animals communicate with each other?
Animals use a variety of communication methods, including vocalizations, body language, and chemical signals. Vocalizations can range from simple calls to complex songs, and they serve different purposes such as warning others of danger or attracting mates. Body language, such as postures and gestures, can convey emotions, dominance, or submission. Chemical signals, like scent marking, help animals establish territory and identify individuals.
Are there any similarities between animal and human communication?
Yes, there are several similarities between animal and human communication. Both animals and humans use vocalizations, body language, and facial expressions to convey their intentions and emotions. Additionally, both rely on visual and auditory cues to understand and interpret the messages being communicated.
Can animals understand human language?
While animals cannot understand human language in the same way we do, some species can learn to associate specific sounds or words with certain actions or rewards. For example, dogs can be trained to respond to verbal commands like "sit" or "stay." However, their comprehension is limited to simple commands and they do not possess the complex language abilities of humans.
What are the main challenges in deciphering animal communication?
Deciphering animal communication poses several challenges for researchers. One of the main challenges is that animals use different sensory modalities and signals depending on their species and environment. Additionally, many animal communication signals are subtle and require careful observation and analysis. Furthermore, understanding the meaning and context of these signals can be complex as they may vary among individuals or groups within a species.
What is the focus of the article "Dream of a Communicative Tiger: Unlocking the Secrets of Animal Communication"?
The focus of the article is to explore animal communication and the efforts made to decipher and understand it.



