Within the depths of the human mind lies a realm brimming with ethereal landscapes, where the boundaries of reality blur, and the subconscious takes center stage. However, nestled amidst these nocturnal realms, there exists an enigmatic phenomenon that often imposes its presence in the realm of dreams, causing perplexity and unease. This phenomenon, originating from within the intricate network of the auricular canal, engenders a plethora of enigmatic impressions and distressing imagery, leaving the dreamer bewildered and perturbed.
Behold the anatomical structure responsible for these disconcerting visions - the auricular receptacle. This intricate assemblage, encased in flesh, harbors a labyrinthine network of sensory apparatus, which perceives the auditory world and resonates with vibrations from beyond. When this sanctuary of sound becomes compromised, a cascade of uncharted sensations infiltrate the slumbering mind, unveiling an unsettling symphony of interpretations.
At the core of these nocturnal enigmas lies an imperceptible intruder - a condition whose manifestations manifest not in the physical realm but rather in the diaphanous fabric of dreams. This elusive ailment, shrouded in uncertainty, beckons us to embark upon a journey of understanding, to decipher the enigmatic inklings woven into the nocturnal tapestry. It is this quest that compels us to unravel the origins, discern the telltale signs, and explore the myriad of remedies available to aid those who find themselves ensnared by the clutches of this perplexing ailment.
Understanding the Spread: How the Infection is Contracted and Transmitted
When it comes to comprehending the transmission of infections within the context of a person's ear, it is crucial to delve into the intricacies of how these unpleasant conditions are contracted and spread. Understanding the various avenues through which an ear infection can be contracted is essential in order to mitigate the risk and prevent further complications.
In the majority of cases, the onset of an ear infection is caused by pathogenic microorganisms that find their way into the ear canal. These microorganisms can be bacteria, viruses, or fungi, and they tend to enter the ear through different means. One of the most common ways an ear infection is contracted is through direct contact with an infected person's respiratory secretions. This can occur through close proximity during conversations, kissing, sharing of personal items like headphones or earphones, or even during medical procedures involving the ear.
- Respiratory secretions: Close contact with an infected individual can result in the transference of bacteria or viruses from their respiratory secretions into the ear. Coughing, sneezing, or talking can expel these respiratory droplets, which can then find their way into the ear canal.
- Swimming and water-related activities: Prolonged exposure to water, especially in contaminated swimming pools, hot tubs, or natural bodies of water, can increase the risk of contracting an ear infection. Moisture provides an optimal environment for bacteria or fungi to thrive, and when water enters the ear canal, it can create a breeding ground for infection.
- Foreign objects: Inserting objects, such as cotton swabs or earplugs, into the ear canal can inadvertently introduce bacteria or fungi and disrupt the natural protective mechanisms of the ear, resulting in an infection.
In addition to understanding how an ear infection is contracted, recognizing the modes of transmission is equally important in preventing further spread. If proper precautions are not taken, an ear infection can easily be transmitted from one individual to another. It is crucial to be aware of the following transmission routes:
- Direct contact: Similar to the contracting phase, direct contact with an infected person can result in the spread of an ear infection. Close proximity, physical contact, or sharing personal items can facilitate the transfer of microorganisms from one individual to another.
- Indirect contact: In certain circumstances, an ear infection can be transmitted indirectly through contaminated objects or surfaces. Objects such as earbuds, towels, or bedding that have been in contact with an infected individual's ears can harbor pathogens and act as a source of transmission if not properly cleaned or disinfected.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of both the potential sources of contracting an ear infection and the modes of transmission, individuals can implement preventive measures to minimize the risk of infection. These measures may include practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and maintaining clean and sanitized personal items. By staying informed and proactive, one can take significant steps towards safeguarding their ears from potential infections and promoting overall ear health.
Detecting the Signs: Identifying Symptoms of an Ailing Ear
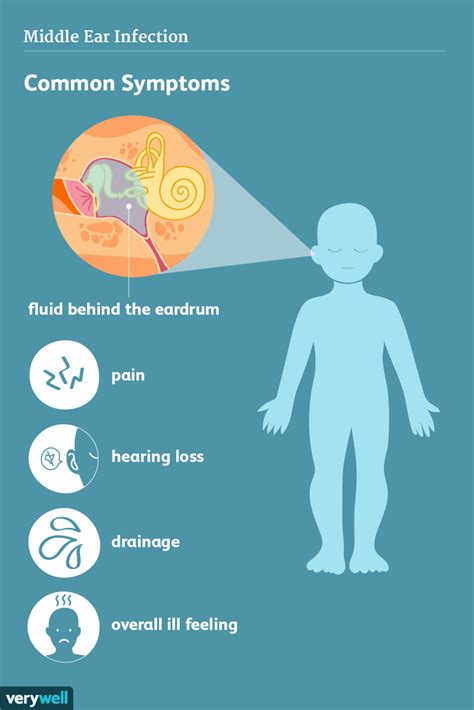
The ability to recognize early signs of an impaired ear is crucial in ensuring timely intervention and effective treatment. By familiarizing yourself with the common indications of an ear infection, you can seek medical attention and alleviate discomfort before it worsens. This section will guide you through the recognition of symptoms associated with an affliction of the ear.
| Telltale Signs | Associated Descriptions |
| Persistent Earache | A continuous, throbbing pain originating from the affected ear |
| Decreased Hearing Ability | Difficulty in perceiving sounds or feeling like the ear is clogged |
| Increased Sensitivity to Noise | An intensified response to everyday sounds, resulting in discomfort |
| Drainage from the Ear | Fluid or pus secretion, often accompanied by an unpleasant odor |
| Ear Fullness or Pressure | A sensation of the ear being stuffed or under increased tension |
| Impaired Balance | Difficulty maintaining equilibrium or a feeling of dizziness |
| Fever | An elevated body temperature, possibly indicative of infection |
While the presence of these symptoms may suggest an ear infection, it is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. Recognizing these signs can contribute to prompt medical care and improved well-being.
Factors Contributing to Ear Infections: Understanding Common Causes
Ear infections can arise due to a multitude of factors that influence their occurrence and severity. By identifying the common causes associated with these infections, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and effectively manage this troubling condition.
- Prolonged exposure to damp environments: Spending prolonged periods in damp environments can increase the likelihood of developing an ear infection. Moisture creates a favorable breeding ground for bacteria and fungi, leading to potential infections.
- Malfunctioning Eustachian tubes: When the Eustachian tubes, responsible for draining fluid from the middle ear into the throat, fail to function effectively, it can result in a buildup of fluid and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Upper respiratory infections: Common colds and respiratory infections can cause congestion and inflammation in the nasal passages and throat, leading to blockages and the spread of bacteria or viruses to the ear.
- Allergies: Seasonal allergies or allergic reactions to certain substances can trigger inflammation and congestion in the nasal passages, creating an environment conducive to ear infections.
- Frequent use of pacifiers or bottles: In infants and young children, excessive use of pacifiers or bottles can disrupt the normal flow of fluids in the ear, leading to fluid accumulation and potential infection.
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke: Tobacco smoke irritates the lining of the Eustachian tubes, impairing their ability to function properly and increasing the risk of ear infections.
- Changes in air pressure: Rapid changes in air pressure, such as during air travel or scuba diving, can cause Eustachian tube dysfunction and create an environment where infections can thrive.
- Age and anatomical factors: Young children, individuals with structural abnormalities in the ear, or those with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to developing ear infections.
By understanding these common causes, individuals can implement preventative measures and consult with medical professionals to effectively manage and minimize the occurrence of ear infections.
Preventive Measures: Tips for Minimizing the Risk of Ear Infections
One of the key aspects of maintaining good ear health is taking proactive steps to prevent ear infections. By implementing simple preventive measures, individuals can reduce the likelihood of developing an infection in their ears. This section highlights some important tips and practices that can help minimize the risk of ear infections, ensuring optimal ear health.
1. Maintain Proper Ear Hygiene: Practicing good ear hygiene is crucial for preventing ear infections. Regularly clean your ears using gentle methods, such as using a damp cloth or cotton swab to remove excess wax. However, be cautious not to insert anything into the ear canal, as it may cause damage or increase the risk of infection. |
2. Avoid Excessive Moisture: Moisture in the ears can create a favorable environment for bacterial or fungal growth, leading to infections. To minimize this risk, take preventive measures to avoid excessive moisture in the ears. Dry your ears thoroughly after swimming, bathing, or any activity that involves water. Use a towel or a hairdryer on a low setting, ensuring that the ears are completely dry. |
3. Practice Healthy Swimming Habits: Swimming can increase the risk of ear infections, especially in cases where water enters the ears. To prevent this, wear earplugs while swimming, particularly in untreated water bodies such as lakes or pools with questionable sanitation. Additionally, consider using a swim cap to minimize water exposure. |
4. Be Mindful of Allergies: Allergies can contribute to ear infections, especially those affecting the respiratory system. In order to reduce the risk, be mindful of any allergies you may have and take appropriate measures to manage them. Consult with a healthcare professional to identify potential allergens and develop an allergy management plan. |
5. Avoid Smoking and Secondhand Smoke: Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can irritate the respiratory system and increase the vulnerability to infections, including ear infections. Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke is not only beneficial for overall health but also contributes to reducing the risk of ear infections. |
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can significantly lower the chances of having an ear infection. Taking care of your ears and following healthy practices will promote optimal ear health and contribute to overall well-being.
Seeking Medical Help: When and Why You Should Consult a Doctor

Seeking professional medical help is crucial when dealing with issues related to your ears. Knowing when to consult a doctor and understanding why it is important can help prevent further complications and ensure effective treatments.
It is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms that warrant a visit to a healthcare professional. Some indicators include persistent discomfort, unusual discharge, hearing loss, and a feeling of fullness in the affected ear. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention promptly.
Consulting a doctor is vital to accurately diagnose and treat any potential ear infections or related problems. A healthcare professional possesses the expertise to identify the underlying causes of your ear issues, distinguish between different types of infections, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
In addition, seeking medical help ensures that you receive the correct prescription medications or therapies tailored to your specific condition. A doctor can prescribe appropriate antibiotics, pain relievers, or eardrops, depending on the severity and type of infection. They can also advise on proper ear care practices to prevent future complications.
Furthermore, a doctor can identify and address any underlying factors that may contribute to recurring or chronic ear infections. By understanding these potential causes, such as allergies, anatomical abnormalities, or excessive moisture exposure, your healthcare provider can develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses the root issues.
Remember, self-diagnosis and self-medication can lead to incorrect treatment and delay in addressing the problem effectively. The expertise and guidance of a doctor are invaluable in ensuring proper management of ear infections, preventing complications, and maintaining optimal ear health.
In summary, when dealing with ear-related problems, it is essential to consult a doctor when experiencing persistent symptoms or discomfort. Seeking medical help allows for accurate diagnosis, proper treatment, and prevention of further complications. So, if you are experiencing any concerning ear issues, don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for assistance and guidance.
Treatment Options: Available Methods to Cure Affected Ears
When dealing with issues concerning the health of our auditory organs, it is of paramount importance to explore the various treatment options that can assist in alleviating the discomfort and addressing the root cause of the problem. In this section, we will delve into the diverse approaches and methodologies that can be employed to effectively treat affected ears.
Medication: One of the primary treatment avenues involves the use of appropriate medications that target the infection causing distress in the ear. These pharmaceutical solutions can come in the form of oral antibiotics, topical ointments, or eardrops. By selecting the most suitable medication, healthcare professionals aim to combat the underlying infection and promote healing.
Complementary Therapies: In addition to conventional medical interventions, certain complementary therapies can be beneficial in restoring ear health. These alternative methods may include the use of herbal remedies, essential oils, or homeopathic treatments. It is crucial to consult with healthcare providers or certified practitioners before initiating any complementary therapies to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
Ear Irrigation: This procedure involves the careful flushing of the ear canal with a warm saline solution or specialized irrigation kits. By gently irrigating the affected ear, accumulated debris, excess earwax, and any infectious agents can be dislodged. Ear irrigation can provide relief for individuals experiencing discomfort or pain resulting from an infected ear.
Surgical Interventions: In rare cases, when conservative treatments prove inadequate, surgical interventions may be deemed necessary. Procedures such as drainage of abscesses, removal of foreign objects or damaged tissues, or even the reconstruction of the affected ear structures may be recommended by medical professionals to address severe or recurrent infections.
Preventive Measures: Alongside the treatment options available, it is essential to maintain good ear hygiene and adopt preventive measures to avert future infections. This can involve practicing proper ear cleaning techniques, avoiding the use of cotton swabs or other objects that can push debris deeper into the ear canal, and regularly examining the ears for any signs of infection or abnormality.
In conclusion, the treatment options for affected ears encompass a range of approaches aimed at eradicating infections, restoring function, and preventing recurrence. By considering the individual needs and circumstances of each case, healthcare providers can determine the most appropriate treatment pathway to ensure optimal ear health and overall well-being.
Lifestyle Changes: Recommended Practices for Maintaining Ear Health

Ensuring the well-being of our ears is crucial for our overall health and quality of life. While the specific causes, symptoms, and treatment options for infected ears are important to address, it is equally vital to focus on preventive measures and lifestyle changes that can help maintain ear health.
1. Protect Your Ears in Noisy Environments
Exposure to loud noises can have detrimental effects on our ears, leading to potential hearing loss or damage. It is essential to take necessary precautions, such as using earplugs or wearing earmuffs, in high-decibel environments like construction sites or concerts.
2. Practice Proper Ear Hygiene
Regular cleaning of our ears is essential, but it should be done with caution. Using cotton swabs or other objects to clean the ears can push earwax deeper into the ear canal, increasing the risk of blockages or infections. Instead, gentle wiping of the outer ear with a clean cloth is recommended.
3. Avoid Inserting Foreign Objects in Your Ears
Inserting objects such as bobby pins, matchsticks, or even fingers into the ears can cause significant harm, including punctured eardrums or damage to delicate structures within the ear. It is crucial to avoid this practice and seek professional assistance if there is any discomfort or blockage.
4. Be Mindful of Water Exposure
Excessive exposure to water, whether through swimming, showering, or bathing, can lead to moisture buildup in the ear, making it a favorable environment for bacterial growth. It is essential to dry the ears thoroughly after water activities, tilt the head to each side, and gently tug the earlobe to facilitate drainage.
5. Quit Smoking
Smoking is not only harmful to the respiratory system but also negatively impacts ear health. Studies have shown that smoking can increase the risk of ear infections, hearing loss, and tinnitus. Quitting smoking or avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke can significantly contribute to maintaining healthier ears.
6. Stay Up-to-Date with Immunizations
Certain infectious diseases, like influenza or pneumococcus, can have complications that affect the ears. Staying updated with recommended immunizations can help prevent some of these infections and reduce the risk of related ear problems.
7. Control Allergies
Allergies, particularly those affecting the upper respiratory system, can often lead to ear problems such as congestion, fluid accumulation, or infections. Managing allergies through appropriate medications or allergen avoidance can help alleviate the associated ear issues.
8. Consult with an Ear Specialist
If you experience persistent ear discomfort, pain, or any concerning symptoms, it is crucial to consult with an ear specialist or otolaryngologist. They can provide proper diagnosis, advice, and personalized recommendations to ensure optimum ear health.
By incorporating these recommended practices into our lifestyle, we can significantly contribute to the maintenance of healthy ears and reduce the risk of various ear conditions. It is essential to prioritize ear health and adopt preventive measures to enjoy a life filled with clear and unimpeded hearing.
FAQ
What are the common causes of an infected ear?
The common causes of an infected ear include bacterial or viral infections, swimmer's ear, allergies, and skin conditions.
What are the symptoms of an infected ear?
The symptoms of an infected ear may include ear pain, swelling, redness, itching, discharge, hearing loss, and a feeling of fullness in the ear.
How is an infected ear treated?
The treatment for an infected ear depends on the underlying cause. It may involve antibiotics, antiviral medications, ear drops, pain relievers, or in severe cases, surgery.



