In a world filled with unlimited possibilities, our imaginations soar as we contemplate the concept of duplicating ourselves. This fascination with the duplication of human life has emerged as an enigmatic realm, a realm that captivates minds and stirs emotions. Invoking a sense of awe and curiosity, the idea of replicating oneself has evolved from science fiction lore into a topic of profound contemplation and scientific exploration.
Unveiling a plethora of potential implications, the prospect of embracing a replicated self has ignited debates that traverse ethical, societal, and philosophical boundaries. This notion not only challenges our fundamental understanding of identity and individuality, but it also beckons us to redefine the very essence of what it means to be human. The spectacle of a self not confined by temporal and spatial limitations awakens a desire within us to transcend the boundaries of mortality and experience life in a profoundly distinctive way.
With its roots interwoven in ancient mythology and modern scientific breakthroughs, this concept instills a sense of wonder and excitement within us. It evokes questions about the nature of consciousness, the potential for immortality, and the interconnectedness of all things. As we delve deeper into the realms of genetics, artificial intelligence, and human psychology, we inch closer to unlocking the secrets behind the dream of being replicated.
However, this fascination does not come without deep-seated concerns. As we envision the possibility of creating replicas of ourselves, the ethical implications become impossible to ignore. Questions of consent, individual agency, and existential repercussions loom large. The responsibility of not only creating, but also nurturing these replicas demands an examination of our ethical framework in unprecedented ways. It forces us to take a momentous step back and re-evaluate our understanding of personhood, autonomy, and the delicate balance between progress and responsibility.
The Concept of Cloning: Embracing the Science Behind Replication

Within the realm of scientific exploration lies an intriguing concept that captivates the imagination and arouses curiosity: cloning. This remarkable area of study delves into the replication of living beings, igniting a multitude of possibilities and ethical debates. By delving into the science behind cloning, we can unravel the intricacies of this phenomenon and gain a clearer understanding of its implications.
Contemplating the idea of cloning involves contemplating the notion of creating an exact genetic replica of a living organism. Through the manipulation of cells and genes, scientists endeavor to duplicate the unique characteristics, traits, and even memories of living creatures. The process of cloning requires extraordinary precision, demanding the utmost accuracy in recreating the intricate blueprint of life.
Cloning can occur naturally, as evidenced by the replication of plants through vegetative propagation, or it can be achieved artificially in laboratory settings. Recognizing the significance of genetic makeup, scientists meticulously extract and transfer genetic material to initiate the replication process. By utilizing various techniques such as somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) or induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), they aim to recreate an organism that possesses the same genetic composition as its parent.
While cloning holds the potential for countless advancements in fields such as medicine and agriculture, it also raises ethical concerns and prompts discussions on the boundaries of science. Questions regarding the implications of human cloning, the rights of cloned organisms, and the potential for misuse of this technology stir both excitement and apprehension. Approaching the concept of cloning necessitates a deep understanding of the science behind it and an open dialogue to explore its far-reaching consequences.
Cloning in Pop Culture: Depicting Replication in Movies and Literature
In the vast realm of popular culture, cloning has emerged as a captivating theme, enthralling audiences and inviting contemplation about the ethical, scientific, and existential implications of replication. This sub-section explores the portrayal of cloning in various forms of media, including films and literature, offering audiences a window into the intriguing world of duplicates and genetic engineering.
Film adaptations: Movies have long been a medium through which the fascination with cloning has been explored. From thought-provoking philosophical pieces to thrilling science fiction narratives, filmmakers have delved into the concept of replication, often raising questions about identity, individuality, and the consequences of tampering with nature. Notable examples include the timeless classics Blade Runner, The Island, and Never Let Me Go, where clones serve as central characters, inviting audiences to reflect upon the human experience and the definition of self.
Cloning in literature: Beyond the silver screen, cloning has also found its place in literature. Writers have utilized the power of words to delve into the depths of scientific advancements and their impact on society. Reflecting a range of genres, including dystopian fiction, speculative fiction, and even romance, novels such as Brave New World by Aldous Huxley and Neverwhere by Neil Gaiman explore the complexities of cloning, often intertwining it with broader themes of power, control, and societal manipulation.
Ethical dilemmas: The representation of cloning in popular culture is invariably intertwined with ethical questions. The portrayal of clones as mere copies raises concerns about the autonomy and rights of these creations. Furthermore, the manipulation and control of cloned beings by those in power serve as cautionary tales about the abuse of scientific advancements. Through these narratives, audiences are prompted to reflect on the moral implications of cloning and its potential consequences for humanity.
In conclusion, the depiction of cloning in films and literature offers a rich exploration of the intricacies and implications of replication. These stories not only captivate audiences with their imaginative narratives but also encourage thoughtful contemplation about the boundaries of science and the essence of humanity.
Ethical Considerations: The Moral Dilemmas Surrounding Cloning
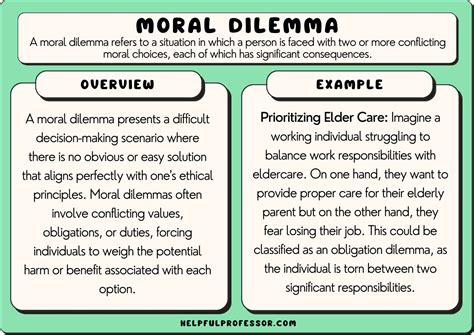
When it comes to cloning, there are complex ethical considerations that give rise to moral dilemmas. The creation of identical copies of living organisms raises questions about the intrinsic value and uniqueness of life, the boundaries of scientific manipulation, and the potential consequences of human intervention in the natural order.
One of the primary ethical concerns surrounding cloning is the violation of individuality and personal identity. Cloning challenges the belief that every living being is inherently unique and possesses a singular identity. By replicating an organism, whether it be a human or an animal, we blur the lines between what is natural and what is artificially engineered. This raises questions about the essence of existence and the significance of individual experiences.
Another ethical consideration revolves around the potential social implications of cloning. The ability to create genetically identical copies of individuals can lead to a loss of diversity within populations. This homogenization could have far-reaching effects on ecosystems, as well as societal structures and dynamics. Additionally, cloning raises concerns about the possibility of using genetic replication as a means of creating a superior or privileged class, further exacerbating social inequalities.
The moral dilemmas surrounding cloning also extend to issues of consent and autonomy. Cloning involves manipulating genetic material without the explicit consent of the cloned individual. This raises profound questions about the rights of the clone and their ability to make choices regarding their own existence. Furthermore, the creation of cloned beings raises concerns about the potential for exploitation and the commodification of life.
Overall, the ethical considerations surrounding cloning are multifaceted and provoke deep moral introspection. As science continues to progress and the boundaries of what is possible expand, it becomes increasingly important to navigate these dilemmas with thoughtfulness and care. Balancing scientific advancements with respect for the intrinsic value of life is a crucial challenge that society must grapple with as we explore the frontiers of cloning technology.
| Examples of Ethical Considerations: |
| 1. Violation of individuality and personal identity |
| 2. Potential loss of diversity within populations |
| 3. Social implications and exacerbation of inequalities |
| 4. Issues of consent and autonomy |
| 5. Potential for exploitation and commodification of life |
Unleashing the Potential for Medical Breakthroughs: Exploring Cloning and Genetic Engineering
In this section, we will delve into the far-reaching possibilities that arise from the convergence of cloning and genetic engineering. By combining these innovative technologies, scientists have unlocked a realm of potential for groundbreaking advancements in the field of medicine. The ability to manipulate genes and replicate living organisms at a cellular level holds immense promise for the treatment of diseases, the development of new drugs, and even the creation of engineered tissues and organs.
Revolutionizing Disease Treatment: Cloning and genetic engineering have the power to revolutionize the treatment of various diseases. By targeting specific genes or altering genetic codes, scientists can potentially eradicate genetic disorders and hereditary diseases that have plagued humanity for generations. This scientific advancement offers hope for individuals and families burdened with conditions that were previously considered untreatable or incurable, paving the way for a healthier and brighter future.
Pioneering New Drug Development: The fusion of cloning and genetic engineering presents a unique opportunity to pioneer the development of new drugs. By creating cloned organisms with specific genetic traits, scientists can study and understand the mechanisms of diseases more comprehensively. This deeper understanding allows for the identification and testing of innovative therapeutic interventions, potentially resulting in the discovery of ground-breaking pharmaceuticals that target specific diseases with unprecedented precision.
Engineering Tissues and Organs: Another exciting application of cloning and genetic engineering lies in the creation of engineered tissues and organs. Through the manipulation of cells and their genetic material, scientists have the potential to cultivate organs and tissues for transplantation without the need for donors. This promises to alleviate the global shortage of organs available for transplantation, providing a life-saving solution to countless individuals awaiting critical medical interventions.
In conclusion, the convergence of cloning and genetic engineering represents a revolution in the field of medicine. By unleashing the potential for medical breakthroughs, these technologies offer hope for disease treatment, the development of new drugs, and the provision of life-saving organs and tissues. As science and technology continue to advance, the possibilities for improving human health and well-being through cloning and genetic engineering are truly awe-inspiring.
Reviving Extinct Species: Could We Resurrect the Dinosaurs?

In this section, we delve into the realm of possibilities regarding the cloning of extinct species, specifically focusing on the intriguing idea of bringing back the long-lost dinosaurs.
Imagine a world where the once mighty giants roam the earth once more. This concept has captivated the imagination of both scientists and enthusiasts alike, sparking a search for ancient DNA that could potentially make this once-fictional dream a reality. Through the utilization of cutting-edge biotechnology, researchers have begun to explore the feasibility of resurrecting extinct species, with dinosaurs being at the forefront of these discussions.
While the idea of bringing back dinosaurs may seem like the stuff of science fiction, recent advancements in genetic manipulation and cloning technologies have allowed scientists to seriously contemplate the possibility. By extracting preserved genetic material from fossils, scientists aim to decipher the genetic code of long-extinct species and reconstruct their genomes. This would serve as the first crucial step towards resurrecting these ancient creatures.
However, the challenges of cloning extinct species, particularly dinosaurs, are immense. Even with intact genetic material, scientists would need to find a suitable surrogate species with similar reproductive biology to carry the cloned embryos to term. Additionally, the gaps in ancient DNA and the potential degradation of genetic material over time pose significant obstacles. Despite these challenges, the field of de-extinction remains an active area of research.
- Genetic Engineering: Scientists are investigating the use of genetic engineering techniques to fill in the gaps in dinosaur DNA using close modern-day relatives, creating a hybrid species that closely resembles the extinct dinosaurs.
- Environmental Considerations: Before moving forward with cloning extinct species, researchers must carefully evaluate the potential ecological impact of reintroducing these ancient creatures into their modern-day habitats.
- Ethical and Moral Quandaries: The revival of extinct species raises complex ethical questions, ranging from the welfare of resurrected animals to the implications for biodiversity and conservation efforts.
While the resurrection of dinosaurs remains a topic of speculation and debate, the possibilities opened up by advancements in cloning and genetic engineering cannot be ignored. Exploring the potential for resurrecting extinct species not only brings us closer to understanding Earth's history but also forces us to confront the ethical, scientific, and philosophical implications of playing with the very fabric of life itself.
Cloning as a Solution: Addressing Global Issues and Challenges
In this section, we will explore the concept of replicating living organisms as a potential solution to various global issues and challenges. By creating identical copies of organisms, cloning opens up new avenues for scientific research, medical advancements, and environmental conservation.
One area where cloning holds promise is in the field of medical transplantation. The shortage of suitable organs for transplantation has been a persistent challenge worldwide. Cloning offers the possibility of generating organs that are genetically identical to the recipient, thereby eliminating the risk of rejection. This can potentially save countless lives and alleviate the burden on transplant waiting lists.
Moreover, cloning can play a crucial role in preserving endangered species and addressing biodiversity loss. By cloning endangered animals, we can prevent their extinction and restore their populations. This approach not only contributes to the conservation of species but also helps maintain the delicate balance of ecosystems. Additionally, cloning can aid in the recovery and rehabilitation of habitats impacted by human activities or natural disasters.
Furthermore, the agricultural sector stands to benefit from the application of cloning techniques. Through cloning, farmers can replicate superior livestock that exhibit desirable traits such as high milk production, disease resistance, or meat quality. This can lead to increased productivity, improved food security, and a reduced environmental impact in the long run. Cloning can also enhance crop production by generating genetically identical plants that are more resilient to pests, diseases, and adverse weather conditions.
However, it is important to acknowledge the ethical considerations associated with cloning. The idea of duplicating living organisms raises questions about individuality, identity, and the potential erosion of diversity. Striking a balance between the scientific advancements enabled by cloning and the preservation of natural variations is crucial to ensure the responsible and sustainable use of this technology.
| Overall, cloning presents a range of possibilities in addressing global challenges. Whether it is through medical advancements, conservation efforts, or agricultural improvements, cloning has the potential to revolutionize various sectors and contribute to a better future for our planet. |
The Future of Cloning: Predictions and Speculations

Exploring the uncharted realm of clone-related possibilities, this section delves into the exciting future that awaits the field of cloning. With a deep dive into predictions and speculations, we examine the potential advancements and ethical challenges cloning might present in the years to come.
Unveiling Boundless Opportunities:
As technologies and scientific understanding continue to evolve, the future of cloning holds immense promise. It is a realm where the boundaries of imagination seem limitless, bringing forth a multitude of potential applications and implications.
Groundbreaking Medical Advancements:
One of the most anticipated areas of progress in cloning is its impact on medical advancements. Researchers believe that advancements in this field may pave the way for groundbreaking breakthroughs in regenerative medicine, organ transplantation, and the treatment of genetic disorders.
Species Preservation and Biodiversity Restoration:
Cloning also has vast implications for conservation efforts and the preservation of endangered species. With continued progress, cloning techniques may offer a lifeline to species on the brink of extinction, providing an opportunity for biodiversity restoration and significant strides towards a more sustainable future.
Ethical Considerations and Controversies:
While the future of cloning holds immense promise, it also raises complex ethical considerations. Discussions around issues related to human cloning, genetic modification, and the potential for misuse demand careful consideration. It is imperative to navigate these debates with a balance of scientific progress and ethical accountability.
Cultural and Societal Ramifications:
As cloning technology progresses, it is crucial to reflect upon its cultural and societal ramifications. Questions regarding identity, familial relationships, and the concept of individuality in a world with clones will undoubtedly shape the conversations and directions we take as a society.
From Science Fiction to Reality:
With all its potential, the future of cloning may turn what was once considered science fiction into reality. As researchers continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding the cloning process, society stands at the precipice of a new era where the possibilities are as captivating as they are controversial.
FAQ
What is the fascination with cloning?
Cloning has always fascinated people due to its potential to create an exact replica of someone or something. The idea of getting a chance to duplicate oneself or bring back a loved one is intriguing to many.
Is human cloning possible?
While human cloning is theoretically possible, it has not been achieved successfully yet. Scientists face numerous ethical and technical challenges in attempting to clone humans, making it a topic of ongoing debate and research.
What are the potential benefits of cloning?
Cloning offers several potential benefits, such as producing organs for transplantation, preserving endangered species, and advancing medical research. It could also allow infertile couples to have genetically related children. However, it also raises ethical concerns and poses risks.
What are the ethical concerns associated with cloning?
Cloning raises various ethical concerns, including issues of identity, individuality, and the potential for exploitation. It challenges traditional notions of family and reproduction, and raises questions about the rights and dignity of cloned individuals. Additionally, there are concerns about the safety and long-term effects of cloning technology.



