When the mind wanders into the realm of slumber, it delves into a mysterious landscape where thoughts intertwine with emotions, forming vivid and often puzzling scenarios. Among the myriad of subjects that can manifest during the realm of dreams, a peculiar phenomenon may occur – the presence of elevated glucose levels. While sleep is typically associated with rest and rejuvenation, the exploration of this intricate dance between blood sugar and the depths of unconsciousness unveils a fascinating connection.
In the vast tapestry of dreams, the human mind weaves a complex web of symbolic representations. These ethereal visions are not mere figments, but rather a reflection of our inner landscapes and physical well-being. Just as dreams can mirror our deepest desires, fears, and emotions, they can also mirror the delicate balance of our body's metabolic processes.
Consider the enigmatic symbols that may arise while roaming the corridors of dreamland: the exploration of unknown territories, the frantic efforts to solve puzzles, or the overwhelming feeling of being chased. These subtle encounters are not uncommon manifestations of an underlying cause – the fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Through symbolism, the subconscious mind endeavors to elucidate the subtle imbalances that may manifest within the physical body.
While dreams serve as cryptic messengers, conveying messages via enigmatic scenarios, they also offer an opportunity for self-reflection and understanding. By unraveling the intricate manifestations that elevate blood sugar in the world of dreams, we can gain insight into potential causes, recognize subtle symptoms, and explore holistic remedies to restore equilibrium. Embark on this enlightening journey as we delve into the captivating interplay between the realms of slumber and our body's intricate metabolic mechanisms.
Understanding High Glucose Levels
In this section, we will explore the intricacies of increased sugar levels in the body and delve into various aspects related to this condition. By comprehending the underlying factors that contribute to elevated glucose in the bloodstream, individuals can gain a better understanding of the potential causes, symptoms, and potential remedies for this health concern.
Unraveling the Mysteries:
Undoubtedly, it is crucial to acquaint ourselves with the nuances associated with heightened blood sugar levels before delving into its causes, signs, and means of managing it. With an aim to shed light on this matter, we will explore the intricate mechanisms that lead to an upsurge in sugar levels, how it affects the body, and the various factors that contribute to this metabolic imbalance.
Gaining Insight into the Symptoms:
Understanding the symptoms associated with high glucose levels can be pivotal in recognizing and addressing the issue promptly. By familiarizing ourselves with the indicators that often manifest in individuals with elevated sugar levels, we can proactively seek appropriate medical support and embark on suitable lifestyle modifications.
Possible Influencing Factors:
Various factors can lead to increased levels of glucose in the bloodstream, extending beyond dietary choices. Discovering these potential triggers enables individuals to gain an encompassing understanding of why their bodies may be manifesting higher glucose levels and potentially aid in constructing a comprehensive management plan.
Exploring Potential Remedies:
While managing high glucose levels is a multifaceted task, a range of potential remedies can help individuals regain control and achieve healthier sugar levels. By exploring methods such as lifestyle modifications, medications, and alternative therapies, individuals can work towards optimizing their overall health and mitigating the long-term impacts of elevated glucose levels.
Conclusion:
By truly understanding the intricacies of elevated glucose levels, individuals can be better equipped to identify potential causes, recognize symptoms, and implement appropriate remedies. This section aims to provide an informative overview and delve into the multifaceted aspects involved in comprehending, managing, and ensuring overall well-being in the face of high blood sugar levels.
Common Triggers of High Glucose Levels
In this section, we will explore the various contributing factors that can lead to elevated blood sugar levels. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can result from a range of agents and lifestyle choices.
Dietary Factors: What we consume plays a significant role in our blood sugar regulation. Consuming excessive amounts of sugary and processed foods can lead to higher glucose levels. Additionally, inadequate fiber intake and overconsumption of carbohydrates can also cause spikes in blood sugar levels.
Physical Inactivity: Sedentary habits and a lack of regular exercise can result in increased blood sugar levels. Physical activity helps the body utilize glucose, lowering its concentration in the blood. In contrast, a sedentary lifestyle can hamper glucose metabolism and lead to higher blood sugar levels.
Stress: Persistent and chronic stress can impact blood sugar levels. When stressed, the body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can interfere with insulin function and cause a rise in blood sugar levels. Consequently, managing stress levels is crucial for maintaining stable blood glucose levels.
Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and diuretics, can contribute to high blood sugar levels. These medications can interfere with insulin production or increase insulin resistance, leading to elevated glucose concentrations.
Insufficient Sleep: Inadequate quality or duration of sleep can negatively impact blood sugar levels. Sleep deprivation can disrupt the body's hormone balance and impair insulin sensitivity, resulting in higher blood sugar levels.
Health Conditions: Various health conditions, such as diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and thyroid disorders, can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels. It is essential to manage these conditions effectively to regulate glucose levels.
By understanding these common causes of high blood sugar levels, individuals can make informed choices to reduce their risk and maintain better control over their glucose levels.
Detecting the Indications of Elevated Blood Glucose

In this section, we will explore how to identify the signs and symptoms that may indicate higher than normal levels of glucose in the blood. Recognizing these indications is crucial for early detection and timely management of elevated blood sugar levels. Without directly mentioning the specific causes, symptoms, or treatments, we will delve into understanding the dawning signs that hint at a potential rise in blood sugar levels.
1. Unusual Thirst: One of the initial signs that may alert individuals about elevated blood sugar levels is an excessive and unquenchable thirst. This sensation of increased desire for fluids could serve as an indication of high glucose concentrations in the body.
2. Frequent Urination: Experiencing a frequent need to urinate, particularly during nighttime, could be another sign of elevated blood sugar levels. Excess glucose in the bloodstream may lead to the kidneys trying to eliminate the sugar through urine, resulting in increased trips to the restroom.
3. Fatigue and Weakness: Unexplained fatigue and weakness may be an early symptom of high blood sugar levels. When glucose isn't properly utilized by the body's cells, it can lead to insufficient energy production, causing individuals to feel tired or lacking strength.
4. Increased Hunger: Feeling consistently hungry, even after eating, can be a potential sign of elevated blood sugar levels. This persistent hunger pangs might be a result of the body's cells not efficiently absorbing glucose, leading to an overall sense of increased appetite.
5. Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden and unexplained weight loss could be a symptom of elevated blood glucose levels, especially when accompanied by increased thirst, hunger, and frequent urination. This unintentional weight loss can occur as the body attempts to compensate for high blood sugar by breaking down fat and muscle for energy.
6. Blurry Vision: Blurred or impaired vision, even transiently, may indicate elevated blood sugar levels. High glucose levels can affect the lens in the eye, leading to temporary changes in vision clarity.
7. Slow Wound Healing: Difficulties in wound healing, such as cuts or bruises taking longer to heal than usual, can be a warning sign of high blood sugar levels. Elevated glucose levels can impair the body's ability to repair damaged tissues efficiently.
It is important to note that experiencing one or more of these symptoms does not necessarily mean having elevated blood sugar levels, as other factors may contribute to these indications. Nevertheless, mindful recognition of these signs can prompt timely medical consultation and necessary steps towards preventive measures or management strategies.
The Connection Between High Blood Glucose Levels and Diabetes
Within the realm of elevated glucose content in the circulatory system lies an intricate correlation with a metabolic disorder known as diabetes. This section delves into the intricate interplay between high blood sugar levels and the onset of diabetes, exploring the underlying connections and implications.
| Understanding Diabetes |
| Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by abnormally high levels of glucose in the blood due to impaired insulin production or utilization. Insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. When the body fails to produce sufficient insulin or becomes resistant to its effects, the concentration of glucose rises, leading to hyperglycemia. |
| Causative Factors |
| Multiple factors contribute to the development of high blood sugar and subsequent diabetes. These include genetic predispositions, sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary choices, obesity, and certain medical conditions. In the absence of appropriate management, these factors can disrupt the delicate equilibrium of glucose homeostasis, triggering a cascade of metabolic dysregulation. |
| Manifestations and Symptoms |
| Elevated blood sugar levels often manifest through several telltale signs, such as frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurry vision, and slow wound healing. These symptoms result from the body's inability to efficiently utilize glucose as an energy source, thereby compromising various physiological processes. |
| Approaches for Diabetes Management |
| Effective management and control of high blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes comprise a multi-faceted approach. Lifestyle modifications, including regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and weight management, play a pivotal role. Additionally, pharmacotherapy, such as the administration of insulin or oral medications, aims to enhance insulin function and regulate glucose levels. Moreover, diligent monitoring of blood sugar levels and periodic medical assessments are crucial in preventing complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes. |
By comprehending the underlying link between high levels of blood glucose and the development of diabetes, individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate risks, promote wellness, and ultimately lead a healthier life.
Long-Term Effects of Uncontrolled Hyperglycemia

When blood sugar levels remain uncontrolled for extended periods, it can lead to a range of detrimental effects on the body. The long-term consequences of persistently high glucose levels go beyond the immediate symptoms and can significantly impact overall health and well-being.
- Cardiovascular complications: Prolonged hyperglycemia can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of developing cardiovascular conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
- Neuropathy: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can result in nerve damage, leading to a condition called diabetic neuropathy. This condition can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the extremities, as well as problems with digestion and urinary function.
- Retinopathy: Persistent high blood sugar can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to a condition known as diabetic retinopathy. It can cause vision problems and, in severe cases, even blindness.
- Kidney disease: Hyperglycemia can impair kidney function over time, leading to the development of diabetic nephropathy. This condition is characterized by kidney damage and can eventually progress to kidney failure.
- Impaired wound healing: Elevated blood sugar levels can hinder the body's ability to heal wounds properly. This can increase the risk of infections, ulcers, and other skin complications.
- Increased risk of infections: Persistently high glucose levels weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, particularly urinary and skin infections.
It is crucial to take proactive measures to control blood sugar levels to minimize the risk of long-term complications. This includes following a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, monitoring blood sugar regularly, taking prescribed medications, and seeking medical advice and support for effective diabetes management.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Adopting a new way of living can have a profound impact on controlling the levels of glucose in your body. By making conscious adjustments to your daily habits, you can effectively manage your blood sugar without relying solely on medications or medical interventions. These lifestyle changes encompass various aspects of your routine and are aimed at improving your overall well-being.
Dietary Modifications: One of the most fundamental changes you can make is to alter your eating habits. Consider incorporating a balanced mix of nutrient-rich foods that are low in refined sugars and carbohydrates. This can help regulate your blood sugar levels, promote satiety, and provide sustained energy throughout the day. Moreover, it is advisable to control portion sizes and establish a regular eating schedule to maintain stability.
Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise can significantly impact your blood sugar management. Physical activity helps your body effectively use insulin, which in turn aids in keeping glucose levels stable. Activities such as brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or any form of aerobic exercise can be beneficial. Strongly consider incorporating at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise into your daily routine.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial when it comes to managing blood sugar levels. Striving for a healthy body mass index (BMI) can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of insulin resistance. Regular commitment to a balanced diet and exercise routine, as mentioned earlier, can greatly assist with weight management.
Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on blood sugar levels. Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies that bring you joy can effectively reduce stress and help stabilize glucose levels.
Smoking Cessation and Limiting Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can have adverse effects on blood sugar levels. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake are crucial steps towards better blood sugar management. Seek professional guidance and support if needed.
Regular Check-ups: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring and managing your blood sugar levels. They can help identify any potential issues and provide personalized advice to help you achieve optimal glucose control.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, you can take control of your blood sugar levels and improve your overall quality of life. Remember, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before making any significant modifications to your routine.
Medications and Insulin Therapy for High Blood Glucose Levels
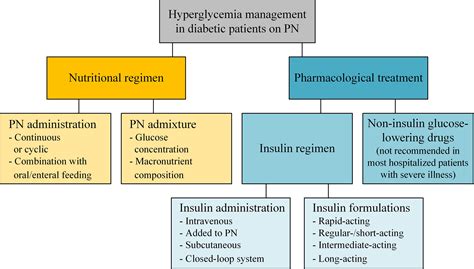
When it comes to managing the increased levels of glucose in the bloodstream, there are various approaches that can be taken to provide effective treatment. Medications and insulin therapy play a crucial role in controlling high blood sugar levels and minimizing the associated complications.
1. Oral Medications:
- Antidiabetic medications
- Hypoglycemic agents
- Glucose-lowering drugs
Oral medications are commonly prescribed to individuals with high blood glucose to enhance insulin production, reduce glucose production in the liver, improve insulin sensitivity, or slow down the absorption of glucose in the intestines.
2. Insulin Therapy:
- Rapid-acting insulin
- Short-acting insulin
- Intermediate-acting insulin
- Long-acting insulin
Insulin therapy plays a vital role in managing high blood sugar levels, particularly for individuals with type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes. Insulin is typically administered through injections or insulin pumps. The choice of insulin type and dosage depends on the individual's specific needs and blood glucose control goals.
3. Combination Therapy:
- Combining oral medications with insulin therapy
- Combining different types of insulin
In some cases, healthcare professionals may recommend a combination of medications and insulin therapy to achieve better blood glucose control. By combining different approaches, it is possible to address multiple aspects of high blood glucose and tailor the treatment to suit individual needs.
It is important to remember that medications and insulin therapy should always be prescribed and monitored by healthcare professionals. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and adjustments in medication dosages are necessary to maintain optimal glucose control and minimize the risk of complications associated with high blood sugar levels.
Natural Solutions for Regulating High Blood Glucose Levels
Addressing elevated blood glucose levels doesn't have to rely solely on pharmaceutical interventions. There are a variety of natural remedies available that can assist in controlling and managing blood sugar levels, promoting overall health and well-being.
Exercise is one of the most effective methods of regulating blood sugar levels. Engaging in regular physical activity can help stimulate the utilization of glucose by the body, assisting in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling can all contribute to improved glucose metabolism.
Incorporating a well-balanced diet rich in fiber and low in processed sugars and carbohydrates is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. Foods such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can provide essential nutrients and help prevent spikes in blood glucose levels. Additionally, incorporating foods with natural blood sugar-regulating properties, such as cinnamon and fenugreek, can enhance the effectiveness of dietary interventions.
Herbal remedies have also shown promise in assisting with blood sugar control. Certain herbs, such as bitter melon, holy basil, and ginseng, are believed to have hypoglycemic effects. These herbs can be consumed in tea or supplement form, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, to support blood sugar regulation.
Managing stress levels is vital for individuals with high blood sugar. Persistent stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which may disrupt insulin production and contribute to blood sugar imbalances. Incorporating stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and regular relaxation practices can help reduce stress and promote optimal blood glucose control.
Finally, adequate sleep is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Lack of sleep or poor sleep quality has been linked to impaired glucose metabolism and increased insulin resistance. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and prioritizing quality sleep can positively impact blood sugar regulation.
| Natural Remedies for Controlling Elevated Blood Sugar |
|---|
| Regular exercise |
| Well-balanced diet |
| Incorporation of blood sugar-regulating foods |
| Herbal remedies |
| Stress management techniques |
| Adequate sleep |
Tips for Preventing Spikes in Glucose Levels

In this section, we will explore practical strategies to avoid experiencing sudden surges in glucose levels. By adopting simple lifestyle changes and making informed choices, you can reduce the risk of encountering fluctuations in your blood sugar levels.
1. Prioritize a Balanced Diet: Opt for a nourishing and well-rounded meal plan that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods. Focusing on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables can help stabilize your blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight.
2. Monitor Carbohydrate Consumption: Be mindful of your carbohydrate intake and choose complex carbohydrates over refined ones. These include foods such as whole grain bread, quinoa, and lentils. Avoid sugary beverages and opt for sugar-free alternatives or water instead.
3. Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise can have a positive impact on your glucose levels. Incorporate both aerobic exercises and strength training into your routine. Consult with your healthcare professional before starting any exercise program to ensure it aligns with your specific needs and capabilities.
4. Stress Management: Chronic stress can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels. Implement stress reduction techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies that relax you. Prioritizing self-care and finding healthy ways to cope with stress can help maintain stable glucose levels.
5. Adequate Sleep: Lack of sleep can disrupt your body's hormone balance, including insulin production. Aim for a consistent sleep schedule and adequate hours of rest each night. If you struggle with sleep issues, consider creating a relaxing bedtime routine and addressing any underlying sleep disorders with a healthcare professional.
6. Regular Monitoring: Stay proactive about monitoring your blood sugar levels. Regularly measure and record your glucose levels as recommended by your healthcare professional. This allows you to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to your diet and lifestyle to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Remember, always consult with a healthcare professional before implementing any changes to your diet, exercise routine, or medication regimen. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure these tips align with your specific health needs and goals.
FAQ
What are some common causes of elevated blood sugar?
There are several common causes of elevated blood sugar, including consuming high-sugar or high-carbohydrate foods, lack of physical activity, stress, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or prediabetes.
What are the symptoms of elevated blood sugar?
The symptoms of elevated blood sugar can vary, but some common ones include frequent urination, increased thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow wound healing, and recurrent infections.
Can elevated blood sugar levels lead to serious complications?
Yes, elevated blood sugar levels can lead to serious complications if left untreated or uncontrolled. Some potential complications include heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, nerve damage, eye problems, and foot problems. It is important to monitor and manage blood sugar levels to prevent these complications.
What are some natural remedies to help lower blood sugar levels?
There are several natural remedies that may help lower blood sugar levels. These include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet rich in fiber and low in sugar, reducing stress levels, getting enough sleep, and incorporating certain herbs and supplements such as cinnamon, chromium, and alpha-lipoic acid. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new remedies.
How can I prevent elevated blood sugar levels?
To prevent elevated blood sugar levels, it is important to make certain lifestyle changes. This includes eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar and high in fiber, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress levels, getting enough sleep, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding tobacco use. Regular blood sugar monitoring and appropriate management of any underlying medical conditions are also crucial preventive measures.
What are the causes of elevated blood sugar levels in dreams?
Elevated blood sugar levels in dreams can be caused by a variety of factors. Stress, anxiety, and certain medications can all contribute to temporary spikes in blood sugar while dreaming. Additionally, individuals with diabetes may experience high blood sugar in their dreams due to their body's inability to regulate glucose levels effectively.



