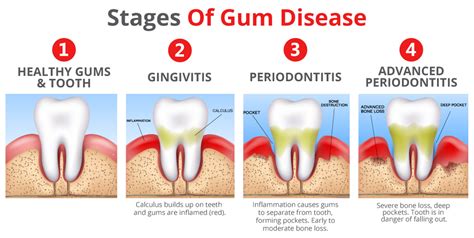
Have you ever experienced vivid and unsettling nocturnal visions pertaining to the well-being of your oral cavity? These perplexing dreams, commonly associated with the presence of infectious microorganisms within the delicate tissues surrounding your teeth, have been observed to manifest in various unsettling forms. While the origins and implications of these enigmatic visions remain a topic of fierce debate within the scientific community, it is crucial to elucidate the factors contributing to their occurrence, discern the telltale indications exhibited, and explore potential avenues for relief.
The etiology of these peculiar dreams is multifaceted, with a myriad of culprits believed to be responsible for their emergence. Factors such as microbial proliferation, compromised oral hygiene practices, or systemic diseases have been postulated as potential triggers. It is essential to recognize that the manifestations of these dreams can differ greatly, ranging from innocuous glimpses of redness and swelling to more distressing portrayals of teeth deterioration and oral discomfort. Nevertheless, the physiological and psychological ramifications connected to these visions should not be dismissed.
Recognition and early identification of the signs associated with dreams of inflamed teeth are of paramount importance. Symptoms may include heightened sensitivity to temperature changes, persistent gum bleeding, foul breath, or the formation of abscesses. These distressing indications should never be disregarded, as delay in seeking appropriate intervention could exacerbate the condition and lead to irreversible consequences. Timely diagnosis, therefore, serves as the gateway to effective treatment and alleviation from the perplexing visions invading your slumber.
Fortunately, a multitude of therapeutic strategies exists to combat the distressing dreams of inflamed teeth. Employing meticulous oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing, flossing, and rinsing with antimicrobial solutions, can aid in the prevention and reduction of bacterial accumulation within the oral cavity. Additionally, consulting with dental professionals, who possess a wealth of expertise in addressing ailments of the oral cavity, can provide valuable insights into personalized treatment plans. These may involve professional cleanings, antibiotics, or, in severe cases, surgical interventions. Embracing a holistic approach and adopting lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet and stress reduction techniques, can further augment the effectiveness of these interventions and pave the way to a dreamless slumber.
The Underlying Factors Behind Gum Infections
Gum infections, also known as periodontal infections, can be caused by a variety of factors. Understanding what triggers these infections is crucial in preventing and treating them effectively.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate dental care, such as infrequent brushing and flossing, can lead to the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth and along the gum line. This buildup creates a favorable environment for bacterial growth, which can eventually result in gum infections.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: The harmful chemicals present in tobacco products not only damage the teeth and gums, but they also weaken the body's immune system. This impaired immune response makes it easier for bacteria to invade and infect the gums.
- Dietary Habits: A diet high in sugary and starchy foods can contribute to gum infections. These types of foods provide an optimal food source for bacteria, allowing them to thrive and multiply within the oral cavity.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during pregnancy or menopause, can increase the susceptibility of gum tissues to infection. This is due to the changes in blood flow and hormone levels that can alter the gum's response to bacteria.
- Chronic Medical Conditions: Certain systemic diseases, such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders, can compromise the body's immune system, making individuals more prone to gum infections. Additionally, certain medications used to manage these conditions can have adverse effects on gum health.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to gum infections. Certain genetic variations can affect the body's ability to fight off bacteria and maintain oral health.
By understanding the underlying causes of gum infections, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent these issues from occurring. Maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding tobacco use, adopting a healthy diet, and seeking regular dental care are essential in reducing the risk of gum infections and promoting overall oral health.
Understanding the Factors Behind Gum Infections
Gum infections are a common dental issue that can cause discomfort and affect oral health. To effectively prevent and treat gum infections, it is crucial to comprehend the underlying factors that contribute to their development. By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with these infections, individuals can take proactive measures to maintain healthy gums.
- Oral Hygiene:
- Tobacco Use:
- Diet:
- Stress:
- Genetics:
Neglecting proper oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing, can significantly increase the risk of gum infections. Inadequate cleaning allows plaque and bacteria to accumulate, leading to inflammation and potential infection.
Smoking or chewing tobacco products not only stains teeth but also weakens the immune system and damages gum tissues. This makes gum infections more likely to occur and harder to combat.
A diet high in sugary foods and beverages can fuel the growth of bacteria in the mouth, promoting gum infections. Consuming nutritious foods and limiting sugary intake is essential for maintaining optimal oral health.
Chronic stress weakens the immune system, making gums more susceptible to infections. Finding effective stress management techniques can contribute to overall gum health.
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to gum infections. Understanding one's family history and genetic factors can aid in taking preventive measures, such as regular dental check-ups and cleanings.
By comprehending the factors mentioned above, individuals can become better equipped to prevent and address gum infections. Establishing a comprehensive oral hygiene routine, making healthy lifestyle choices, and seeking professional dental care regularly are key steps towards maintaining gum health and preventing infections from occurring.
Recognizing Indications of Gum Infections

When it comes to identifying symptoms of gum infections, it is essential to pay close attention to certain signs that may indicate an underlying problem. Although infected gums can manifest in various ways, it is crucial to be aware of these early warning signs to prevent further complications.
One of the key indicators of gum infections is the presence of persistent discomfort or pain in the oral cavity. This discomfort might range from a mild, nagging sensation to severe throbbing pain. Additionally, infected gums often exhibit signs of inflammation, such as redness, swelling, or tenderness. These symptoms are often localized in specific areas of the gums.
Another symptom to be aware of is gum bleeding, especially during routine activities such as brushing or flossing. Infected gums can become more sensitive and vulnerable to bleeding due to increased inflammation and weakened gum tissues. Observing these signs can provide early indications of a potential gum infection.
Furthermore, individuals with infected gums might also experience a change in the appearance of their gum tissue. This could present as a change in color, texture, or even shape. Some individuals may notice that their gums appear redder or darker than usual, while others may observe puffy or receding gums. Any notable changes in the appearance of the gums warrant attention and should be discussed with a dental professional.
Additionally, bad breath or an unpleasant taste in the mouth can also accompany gum infections. The accumulation of bacteria and plaque in the gum pockets can contribute to the development of foul odors and tastes. If you notice persistent bad breath that isn't alleviated by regular oral hygiene practices, it may be an indication of an underlying gum infection.
Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial in the effective management and treatment of gum infections. It is important to consult a dental professional if you experience any of these signs to receive a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Signs That Indicate a Gum Infection: Recognizing the Symptoms
Identifying the early signs of a gum infection is imperative in preventing further complications and ensuring proper treatment. The following indications may suggest the presence of an infection in the gum tissue, without explicit mention of the specific dental condition. Being attentive to these symptoms can help individuals seek timely dental care and improve their oral health.
1. Gum Sensitivity: Feeling tenderness or discomfort in the gum area could be an early warning sign of a potential infection. If your gums become unusually sensitive to touch or pressure, it is essential to consult a dentist for an evaluation.
2. Swollen or Inflamed Gums: Gums that appear red, swollen, or inflamed can be indicative of an underlying infection. Such changes in gum color and texture may require professional dental attention to prevent the infection from spreading.
3. Receding Gums: When the gum tissue starts to pull away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth's surface, it can be a sign of gum infection. Receding gums should be promptly addressed to prevent gum disease progression.
4. Persistent Bad Breath: While occasional bad breath is common, chronic or persistent halitosis can be a sign of an infected gum. The release of unpleasant odors may be a result of bacteria thriving in the gum pockets and can indicate poor oral health.
5. Pain or Discomfort: Feeling pain or discomfort in the gums, especially during eating or brushing, could suggest an underlying infection. Ignoring persistent gum pain can lead to further complications, so seeking dental advice is essential.
6. Bleeding Gums: Experiencing bleeding gums, especially during routine oral hygiene practices, may indicate gum infection. Bleeding gums should not be ignored, as they could be a sign of gum disease or other oral health issues.
7. Formation of Abscesses or Pus: The presence of abscesses or pus pockets on the gums is a clear indication of a severe gum infection. If you notice any pus-filled lesions or swollen areas on your gums, seek immediate dental attention as it may require surgical intervention.
It is crucial to bear in mind that these signs may also overlap with other oral health conditions. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a dental professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Gum Infections
Gum infections can be a bothersome and painful condition that require prompt treatment to prevent further complications. There are various treatment options available to address this issue, each aiming to alleviate discomfort and restore oral health.
1. Antibiotics: In cases where gum infections are caused by bacterial overgrowth or infection, antibiotics may be prescribed by a dental professional. These medications can help eliminate the harmful bacteria and reduce inflammation, promoting healing.
2. Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing): This non-surgical procedure is typically performed by a dental hygienist or periodontist. It involves removing plaque and tartar buildup from below the gumline and smoothing out the tooth roots. Deep cleaning helps eliminate infection-causing bacteria and promotes gum reattachment to the teeth.
3. Gum surgery: In severe cases, gum infections may require surgical intervention. Gum surgery aims to remove infected tissue, reshape the gums, and promote gum reattachment. Procedures such as gum grafting and flap surgery may be performed to restore a healthy oral environment.
4. Antimicrobial mouthwashes: Dental professionals may recommend the use of antimicrobial mouthwashes as an adjunct to other treatments. These mouthwashes contain agents that help control bacterial growth and improve oral hygiene.
5. Oral hygiene practices: Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial in preventing and managing gum infections. Regular brushing, flossing, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help remove plaque and bacteria, reducing the risk of infection.
6. Lifestyle changes: Adopting certain lifestyle changes can also contribute to the treatment of gum infections. Quitting smoking, managing stress levels, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding sugary foods can support gum health and improve overall oral well-being.
7. Regular dental check-ups: Regular visits to a dental professional can help identify and address gum infections early on. Routine dental cleanings and check-ups allow for the early detection of any signs of infection, ensuring prompt treatment.
Overall, timely and appropriate treatment is key to managing and resolving gum infections. It is important to consult a dental professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
FAQ
What are the common causes of infected gums?
Infected gums can be caused by poor oral hygiene, plaque build-up, gum disease, hormonal changes, and certain medications.
What are the symptoms of infected gums?
The symptoms of infected gums include redness, swelling, tenderness, bleeding while brushing or flossing, bad breath, and a bad taste in the mouth.
How can I treat infected gums at home?
You can treat infected gums at home by practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing twice a day, flossing daily, using an antiseptic mouthwash, and avoiding tobacco products.
When should I see a dentist for infected gums?
You should see a dentist for infected gums if the symptoms persist for more than a week, if there is severe pain or swelling, or if you have a high fever. A dentist can diagnose the cause of the infection and provide appropriate treatment.
What are the professional treatments available for infected gums?
Professional treatments for infected gums may include deep cleaning, scaling and root planing, antibiotics, gum surgery, or periodontal therapy, depending on the severity of the infection.
What are some common causes of infected gums?
Common causes of infected gums include poor oral hygiene, plaque buildup, gum disease, tobacco use, certain medications, hormonal changes, and a weakened immune system.



