Within the complex tapestry of human psychology lies a profound fascination with a desire that lurks beneath the surface–a desire to ignite, to fuel the flames, seeking solace in the inferno. This enigmatic propensity, pulsating within the depths of the subconscious, has long stirred the curiosity of minds yearning to understand the intricacies of human nature.
In the realm of cognition, where dreams play a pivotal role, an unconscious force beckons individuals towards scenarios where objects, ideas, or even their own aspirations are engulfed in a cascading conflagration. This compulsion is much like an ember that smolders within, enticing one towards the mysterious allure of destruction and transformation.
With each flicker of an internal flame, this inexplicable urge reveals itself in multifaceted ways, leaving an indelible mark on the human psyche. From ancient myths that depict the gods' insatiable craving for chaos and rebirth, to modern literature and cinema, where protagonists are driven by an indomitable impulse to set their world ablaze–these narratives serve as a testament to the universality of this endlessly enthralling theme.
The Intrigue of Fire: Delving into Pyromania as a Psychological Phenomenon

Within the realm of human behavior, there exists an enigmatic fascination with the element of fire that captivates some individuals to an intense degree. This captivating psychological phenomenon, known as pyromania, unveils a realm of intricate emotions, compulsions, and desires that surround the act of setting fires. The allure of fire, with its mesmerizing dance of flames, engenders a unique and complex psychological response in those afflicted by pyromania.
From Childhood Curiosity to Adult Compulsion: Tracing the Origins of Pyromaniac Tendencies
The journey from childhood to adulthood is marked by various experiences and discoveries, many of which contribute to shaping an individual's personality and behaviors. One such phenomenon that has intrigued psychologists and researchers is the development of pyromaniac tendencies, characterized by an irresistible urge to start fires. This article delves into the origins of this unique compulsion, tracing its roots back to childhood curiosity and exploring the psychological factors that influence its progression into adulthood.
Pyromaniac tendencies often originate from an early childhood fascination with fire. It is not uncommon for children to exhibit curiosity about fire, being naturally drawn to its warmth, light, and movement. However, in some individuals, this curiosity evolves into an obsessive interest, leading to a preoccupation with fire-related activities and an eventual compulsion to ignite flames. Factors such as a lack of parental supervision, exposure to fire-related trauma, or psychological disorders may contribute to the intensification of this fascination.
A key aspect in understanding the progression of pyromaniac tendencies is the influence of psychological development. As children with a curiosity for fire enter adolescence and adulthood, their emotional and cognitive processes undergo significant changes. The transition from childhood to adulthood entails gaining a better understanding of the consequences of one's actions, developing empathy, and adopting a sense of responsibility. However, in individuals with pyromaniac tendencies, these developmental milestones may be hindered or distorted, leading to a persistent attraction to fire and an inability to control or resist the urge to ignite flames.
Environmental factors also play a crucial role in the evolution of pyromaniac tendencies. Growing up in an environment with a high prevalence of fire-related incidents or where fire is glamorized can reinforce and normalize the fascination with fire. Additionally, personal experiences of trauma, neglect, or abuse can further fuel the compulsion to set fires as individuals may seek to exert control or release emotions through these destructive acts.
Understanding the origins of pyromaniac tendencies is essential for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. Early identification of childhood curiosity and appropriate parental guidance can help redirect the fascination with fire towards safer outlets and promote the development of healthy coping mechanisms. Furthermore, recognizing the impact of psychological and environmental factors can assist in providing targeted support and therapy to individuals with pyromaniac tendencies, addressing their underlying issues and managing their compulsion.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| - Pyromaniac tendencies trace back to childhood curiosity and fascination with fire. |
| - Psychological development plays a significant role in the progression of these tendencies. |
| - Environmental factors, such as trauma or exposure to fire-related incidents, can reinforce pyromaniac tendencies. |
| - Understanding the origins is crucial for prevention and intervention strategies. |
Beyond the Flame: Understanding the Intricate Motivations of Those Attracted to Fire

In this segment, we delve into the multifaceted motivations that underlie the attraction individuals feel towards fire, going beyond the fiery spectacle itself. By exploring the intricate psychological factors that contribute to this fascination, we aim to shed light on the complex nature of this phenomenon.
Mental Health and Pyromania: Investigating the Connection between Fire-Setting and Psychological Disorders
Understanding the correlation between the act of arson and mental health conditions is a crucial step towards unraveling the complexities of pyromania. By delving into the intricate relationship between the deliberate use of fire and various psychological disorders, we can gain valuable insights into the underlying factors that may contribute to this dangerous behavior.
Pyromania: a psychological disorder marked by an uncontrollable and recurring urge to set fires, has long been associated with significant disturbances in mental health. While the exact causes of pyromania remain elusive, researchers have posited that it could be linked to various psychiatric conditions, including but not limited to impulse control disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and antisocial personality disorder.
Impulse control disorders, characterized by the inability to resist urges or impulses that may be harmful, are often observed in individuals with pyromania. These disorders encompass a range of conditions, such as intermittent explosive disorder and kleptomania, which share common features with pyromania in terms of the inability to control impulsive behavior.
OCD, a psychiatric disorder characterized by intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors, has also been associated with pyromania. Individuals with OCD may experience obsessive thoughts related to fire-setting and engage in rituals or compulsions linked to these thoughts. Understanding the relationship between OCD and pyromania can provide valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of this destructive behavior.
Furthermore, antisocial personality disorder has been noted as a potential contributing factor to pyromania. Individuals with this disorder often exhibit a disregard for the rights of others and a lack of empathy or remorse for their actions. The destructive nature of fire-setting and the potential harm it inflicts on others align with the characteristics of antisocial personality disorder.
In conclusion, investigating the link between pyromania and mental health disorders offers a comprehensive understanding of the psychological factors underlying the urge to set things on fire. By exploring the intricate associations with impulse control disorders, OCD, and antisocial personality disorder, we can further our knowledge and potentially develop effective interventions for individuals grappling with this dangerous compulsion.
The Impact of Childhood Trauma on Pyromaniac Behaviors: Analyzing the Role of Early Life Adversity
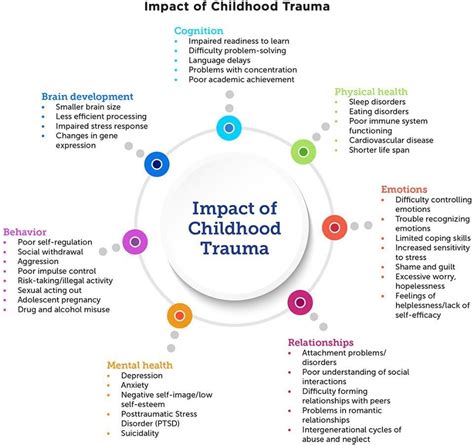
Understanding the factors that contribute to pyromaniac behaviors is crucial in order to develop effective prevention and intervention strategies. One important area of investigation is the role of childhood adversity, as it has been suggested that individuals who engage in fire-setting behaviors may have experienced traumatic events during their early years. This section delves into the influence of childhood trauma on pyromaniac tendencies, exploring the potential mechanisms through which adverse experiences may shape and contribute to this dangerous psychological urge.
| Subtopic 1: Types of Childhood Adversity |
| 1.1 Emotional Abuse: Examining the correlation between emotional abuse and later pyromaniac behaviors. |
| 1.2 Physical Abuse: Investigating the link between physical abuse during childhood and the development of pyromaniac tendencies. |
| 1.3 Neglect: Analyzing the potential role of neglect as a precursor to pyromaniac behaviors. |
The first subtopic focuses on different types of childhood adversity and their potential impact on the development of pyromaniac behaviors. This section explores the specific effects of emotional abuse, physical abuse, and neglect, shedding light on the unique ways in which each type of adversity may contribute to the manifestation of the urge to set things on fire.
| Subtopic 2: Psychological and Neurobiological Mechanisms |
| 2.1 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Investigating the relationship between PTSD and pyromaniac behaviors as a result of childhood trauma. |
| 2.2 Impulsivity and Emotion Dysregulation: Exploring the role of impulsivity and difficulty in regulating emotions in individuals with a history of childhood trauma and pyromaniac tendencies. |
| 2.3 Cognitive Distortions: Analyzing the presence of distorted thinking patterns among individuals who engage in fire-setting behaviors and have experienced childhood adversity. |
The second subtopic delves into the psychological and neurobiological mechanisms that may underlie the relationship between childhood trauma and pyromaniac behaviors. This section examines the potential influence of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), difficulties in emotion regulation, impulsivity, and cognitive distortions, aiming to unravel the intricate connections between these factors and the urge to set things ablaze.
Is Pyromania a Substance-Related Disorder? Unveiling the Link between Fire-Setting and Substance Abuse
Exploring the intricate relationship between pyromania and substance abuse reveals valuable insights into the inner workings of the human mind. This section aims to uncover whether pyromania can be classified as a substance-related disorder, examining the potential connection between fire-setting behaviors and substance abuse.
Pyromania: A phenomenon characterized by an intense fascination or obsession with fire, leading to intentional and repetitive fire-setting behaviors. It is important to delve deeper into the psychological underpinnings of this disorder to understand its potential relationship with substance abuse.
Substance-Related Disorders: A range of conditions related to the abuse or dependence on substances such as drugs or alcohol. These disorders significantly impact an individual's physical and mental health, as well as their social and occupational functioning.
While pyromania is traditionally not classified as a substance-related disorder, certain parallels can be drawn between fire-setting behaviors and substance abuse. Both involve a compulsive urge to engage in the behavior despite its adverse consequences, indicating potential shared psychological mechanisms.
Pyromania can be seen as an attempt to satisfy underlying psychological needs or to cope with emotional distress. Similarly, substance abuse often serves as a means of escape or self-medication for individuals facing various challenges or psychological burdens.
Studies have suggested that individuals with pyromania may experience heightened levels of arousal and excitement during fire-setting incidents, similar to the pleasurable sensations associated with substance abuse. This similarity in the rewarding aspects of these behaviors further supports the hypothesis of a potential association between pyromania and substance-related disorders.
Furthermore, it is essential to assess the presence of co-occurring psychiatric conditions, as individuals with both pyromania and substance abuse disorders often exhibit comorbidity. These co-occurring disorders may share common risk factors or underlying neurobiological mechanisms that contribute to the overlap between pyromania and substance-related disorders.
Identifying the relationship between pyromania and substance abuse can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of both phenomena, allowing for improved assessment, diagnosis, and treatment approaches.
In conclusion, while not traditionally classified as a substance-related disorder, pyromania shares similarities with substance abuse. Examining the potential connections between fire-setting behaviors and substance abuse provides valuable insights into the complex interplay of psychological factors. Further research is needed to unravel the intricate relationship between these phenomena and enhance our understanding of the psychological and neurobiological mechanisms involved.
Treatment Approaches: Exploring Effective Therapies for Pyromaniacs to Overcome Their Urges

In this section, we will delve into various approaches aimed at helping individuals with pyromania overcome their destructive urges. By examining different therapeutic modalities, we can gain a deeper understanding of how professionals address the underlying issues associated with this behavioral disorder.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): One commonly utilized approach is CBT, which focuses on identifying and modifying thoughts and behaviors that contribute to pyromaniac tendencies. This therapy aims to challenge and restructure distorted beliefs, replacing them with more rational and healthier ones.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT combines elements of CBT with mindfulness and acceptance techniques. By enhancing emotional regulation skills, DBT helps pyromaniacs cope with intense emotions and develop healthier strategies to manage their urges.
- Group Therapy: Group therapy provides a supportive environment where individuals with pyromania can share their experiences, learn from others, and receive feedback. It offers a sense of community and fosters solidarity among individuals who struggle with similar challenges.
- Pharmacological Interventions: Medication may be prescribed as a complementary treatment to psychotherapy. Certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or mood stabilizers, may help regulate impulsive tendencies and manage underlying mental health conditions.
- Art Therapy: Engaging in artistic activities can serve as a therapeutic outlet to express emotions and explore underlying issues. Art therapy allows individuals with pyromania to explore alternative ways of coping with their urges and gain insights into their destructive patterns.
It is important to note that treatment approaches may vary based on individual needs and the severity of the pyromaniac tendencies. A comprehensive assessment by a mental health professional is crucial for designing an effective treatment plan tailored to each person's unique circumstances. By combining various therapeutic modalities and individualizing treatment, professionals aim to empower pyromaniacs to regain control over their urges and live healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Legal Consequences: Exploring the Legal Ramifications for Individuals Convicted of Fire-Setting Offenses
In this section, we delve into the legal repercussions faced by those who have been found guilty of engaging in fire-setting crimes.
When individuals succumb to the allure of igniting flames with malicious intent, they not only endanger lives and property, but also expose themselves to severe legal ramifications. Fire setting, a behavior characterized by deliberately starting fires outside controlled environments, is regarded as a criminal offense in numerous jurisdictions worldwide. In light of the potentially catastrophic consequences, legislatures have established stringent laws and regulations to address such actions and hold accountable those responsible.
Penalties and Sentencing:
Offenders convicted of fire-setting crimes can expect to face a range of penalties depending on the jurisdiction and severity of the offense. These penalties may include but are not limited to fines, probation, mandatory counseling or therapy, community service, and imprisonment. The severity of the penalties is often influenced by the scope of the damage caused, the presence of injuries or fatalities, and the individual's criminal history.
Legal Classifications:
Fire-setting crimes are commonly classified into various categories based on factors such as intent, context, and impact. Arson, the most severe form of fire setting, typically involves the intentional and malicious act of setting fire to structures or property. Other classifications may include reckless burning, which refers to the act of setting fires with disregard for the potential consequences, and criminal negligence, where the individual's negligent behavior leads to a fire. These distinctions often play a crucial role in determining the specific charges and subsequent legal consequences.
Legal Proceedings and Rehabilitation:
Following an arrest, individuals accused of fire-setting offenses go through a legal process that involves investigations, substantiation of evidence, and court hearings. The objective of these legal proceedings is to establish guilt or innocence and administer appropriate legal consequences. Additionally, the judicial system often seeks to incorporate rehabilitative measures to address underlying psychological factors that may contribute to fire-setting behavior. Offenders may be required to undergo counseling, therapy, or participate in educational programs aimed at addressing their motivations and preventing future recurrences.
Long-term Ramifications:
Being convicted of a fire-setting crime can have long-lasting consequences beyond immediate legal penalties. The stigma associated with such offenses may impact an individual's employment prospects, housing options, and personal relationships. Additionally, individuals found guilty of these crimes may face restrictions on their access to flammable materials or areas where fires are prone to occur. The aim of these long-term ramifications is to deter individuals from engaging in fire-setting activities and to protect society at large.
In conclusion, the legal ramifications for individuals convicted of fire-setting crimes are far-reaching and serve as a deterrent against this dangerous and destructive behavior. It is paramount that individuals understand the severe consequences they may face if they choose to succumb to the urge to set things ablaze.
Preventing Fires: Exploring Approaches to Identifying and Managing Individuals with Pyromaniacal Tendencies

In this section, we delve into the strategies and techniques that can be employed for the purpose of identifying and effectively managing individuals who exhibit pyromaniacal tendencies within society.
Pyromania, a psychological condition characterized by an intense fascination with fire and the act of deliberately setting fires, poses significant risks to both individuals and property. By understanding the underlying factors and implementing targeted approaches, it becomes possible to mitigate these risks and prevent potential harm.
1. Psychological Assessment: A crucial step in identifying potential pyromaniacs is conducting comprehensive psychological assessments. These assessments employ various diagnostic tools to evaluate an individual's thoughts, emotions, and behavioral patterns, enabling professionals to identify any underlying pyromaniacal tendencies.
2. Early Intervention: Timely intervention is key in managing pyromaniacs before they engage in destructive acts. Early detection and intervention can significantly reduce the likelihood of fires being set and prevent potential harm to both the individual and the community at large. This involves implementing intervention programs specifically tailored to address the unique needs and challenges associated with pyromaniacal tendencies.
3. Education and Awareness: Spreading awareness about pyromania and its potential dangers is vital for preventing fires and supporting affected individuals. By educating communities, schools, and relevant stakeholders about the nature of pyromania and the associated risks, it becomes possible to foster a proactive approach towards prevention and intervention.
4. Collaborative Efforts: Addressing pyromaniacal tendencies requires a collaborative approach that involves multiple stakeholders such as mental health professionals, law enforcement agencies, educators, and community members. By working together, these entities can share resources, expertise, and information, leading to a more comprehensive and effective response towards managing pyromaniacs in society.
5. Support and Rehabilitation: For individuals who have already engaged in fire-setting behaviors, providing appropriate support and rehabilitation programs is crucial. These programs aim to address the underlying psychological factors contributing to pyromania, while also equipping individuals with alternative coping mechanisms and skills to manage their impulses in a non-harmful way.
In conclusion, by implementing strategies such as psychological assessments, early intervention, education, collaboration, and support programs, society can better identify, manage, and prevent fires caused by individuals with pyromaniacal tendencies. This comprehensive approach plays a crucial role in safeguarding individuals, properties, and communities from the potential dangers posed by pyromania.
FAQ
Why do some people have dreams of setting things on fire?
There can be several reasons why some individuals have dreams of setting things ablaze. One possible explanation is that these dreams may reflect repressed anger or frustration that the person is experiencing in their waking life. Alternatively, they may symbolize a desire for power or control. It is also important to note that dreams are highly subjective, and their interpretations can vary from person to person.
Is having dreams of setting things on fire a sign of mental illness?
No, having dreams of setting things on fire is not necessarily a sign of mental illness. Dreams are a normal part of the human experience, and they often reflect our emotions, thoughts, and experiences. However, if someone consistently has violent or disturbing dreams, or if these dreams cause significant distress or interfere with their daily functioning, it may be a good idea to consult with a mental health professional to explore any underlying issues.
Do dreams of setting things on fire always have a negative meaning?
No, dreams of setting things on fire do not always have a negative meaning. While they can sometimes be associated with feelings of anger or aggression, dreams can also have positive or neutral interpretations. For example, such dreams might symbolize transformation, letting go of old habits or situations, or the desire for change. The context and personal experiences of the dreamer are important factors in interpreting the meaning of these dreams.
Can recurring dreams of setting things on fire indicate a deeper psychological issue?
Recurring dreams of setting things on fire can potentially indicate a deeper psychological issue. They may be a manifestation of unresolved emotions or traumas, or they could signify a persistent struggle with anger or control. It might be beneficial for individuals experiencing recurring dreams of this nature to consider seeking professional help to explore any underlying psychological issues and gain a better understanding of their dream's significance.
Are there any techniques to cope with dreams of setting things on fire?
Yes, there are techniques that can help cope with dreams of setting things on fire. One approach is to keep a dream journal and write down the details of the dream upon waking. This can help individuals gain insight into their emotions and potentially identify any patterns or triggers. Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, before bedtime, may also promote more peaceful dreams. Additionally, talking to a therapist or counselor can provide valuable guidance and support in understanding and addressing the underlying psychological aspects of these dreams.
What is the article "Dreams of Setting Things Ablaze: Unraveling the Psychology Behind the Urge" about?
The article "Dreams of Setting Things Ablaze: Unraveling the Psychology Behind the Urge" explores the psychology behind the urge to set things on fire.
What factors contribute to the urge of setting things ablaze?
There are several factors that contribute to the urge of setting things ablaze. These include unresolved anger or frustration, a desire for power and control, a fascination with fire, or as a means of communication or expression of emotions.



