Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the remarkable realm of audio storage technology. In this exploration, we will delve into a world where mysterious discs hold the power to preserve and reproduce captivating soundscapes with remarkable precision. As we peer through the lens of curiosity, we will unravel the ingenious construction and evolution of these compact wonders, offering a glimpse into a revolution that forever transformed the way we enjoy music and audio.
Within this realm, the enchanting devices that have captured the hearts of countless music enthusiasts are known by myriad names. Some refer to them as "audio compact discs," while others simply call them "CDs." Regardless of the nomenclature, these technological marvels serve as vessels that safeguard a trove of harmonious melodies, evocative lyrics, and soul-stirring compositions.
With an unwavering commitment to aural fidelity, the era of the compact disc brought forth a profound transformation in the listening experience. Each disc, encased in a protective shell brimming with artistic expression, concealed a breathtaking world of sound awaiting discovery. From hauntingly beautiful classical symphonies to pulsating beats of electronic music, the CD universe caters to every imaginable musical taste, beckoning listeners into a realm of sonic bliss.
Revolutionizing the way we interact with music, the compact disc spared no expense in its pursuit of sonic perfection. Every microscopic detail of a song, every subtle nuance of an artist's voice, was meticulously etched onto the shimmering surface of these discs. With breathtaking precision, lasers dance along the intricate grooves, decoding a symphony of zeroes and ones to reproduce audio with unrivaled clarity.
The Evolution of Optical Sound Storage: From Shiny Discs to Digital Revolution
The chapter explores the captivating journey of optical sound storage mediums, shedding light on the ever-evolving landscape of technology. Delving into the evolution of compact discs, this section unravels the fascinating tale of the humble beginnings, subsequent advancements, and the eventual integration of digital technology.
1. From Vinyl to Compact Discs: Beginning in the late 1970s, compact discs emerged as a revolutionary alternative to vinyl records. This stage recounts the pivotal shift from analog to digital, highlighting the enhanced audio quality and durability offered by CDs.
2. The Birth of CD-ROM: The advent of CD-ROMs in the late 1980s opened up new horizons in data storage and retrieval. This segment delves into the groundbreaking introduction of CD-ROMs, enabling users to store and access vast amounts of information conveniently.
3. CD-R and CD-RW: Rewritable Discs: With CD-R and CD-RW technology, the realm of compact discs expanded its versatility. Exploring the concept of writable discs, this part illustrates the significance of CD-R and CD-RW in facilitating data backups, file sharing, and the emergence of writable optical media.
4. Digital Audio and MP3: The emergence of digital audio and MP3 format revolutionized the music industry. This segment explores the impact of mp3 players and the transformation of portable music players, rendering CDs as a stepping stone towards the digital music era.
5. Beyond CDs: The Rise of Streaming and Digital Downloads: As technology marches forward, this section assesses the contemporary landscape of music consumption. Unveiling the rise of streaming services and digital downloads, it highlights how this technology continues to shape the future of sound storage.
6. The Future: Potential Developments in Optical Media: This concluding portion offers a glimpse into possible future advancements in optical media storage. By presenting potential innovations and trends, it leaves room for imagination regarding the legacy and future of CDs in the ever-evolving world of technology.
From Vinyl to CDs: A Revolutionary Technological Shift
In the world of music, there has been a momentous transformation from the beloved vinyl records to the groundbreaking compact discs. This shift in technology brought about a significant revolution in the way people experienced and consumed music.
Emergence of Compact Discs:
With the advent of compact discs, music lovers found themselves embracing a new era of convenience and innovation. These shiny circular discs, smaller in size compared to vinyl records, revolutionized the way music was recorded, played back, and stored.
Quality and Durability:
Compact discs offered unparalleled audio quality, characterized by crystal-clear sound and diminished background noise. The digital format allowed for a more accurate reproduction of sound, ensuring that listeners could enjoy an enhanced listening experience. Moreover, the durability of CDs minimized the risk of damage, ensuring that music could be preserved and enjoyed for years to come.
Portability and Accessibility:
One of the most remarkable features of compact discs was their portability. Unlike vinyl records, CDs were compact and lightweight, making them easy to carry around and play in various devices, such as CD players, car stereos, and portable personal computers. This newfound portability allowed music enthusiasts to enjoy their favorite tunes anytime, anywhere.
Convenience and Versatility:
CDs also offered a level of convenience that was previously unimaginable. Unlike vinyl records, which required flipping sides and careful handling, CDs allowed for seamless playback and effortless skipping between tracks. Additionally, the digital format of CDs opened up a world of possibilities for music lovers, enabling them to explore new genres, compilations, and curated playlists.
Influence and Legacy:
The introduction of compact discs not only transformed the way music was consumed but also had a profound impact on the music industry as a whole. Artists and record labels embraced this new format, incorporating digital mastering techniques into their recordings to optimize the sound quality for CDs. This technological shift set the stage for further advancements in digital music and paved the way for the digital streaming era we know today.
In conclusion, the transition from vinyl records to compact discs marked a pivotal moment in the history of music. The advent of CDs brought forth a new era of convenience, portability, and audio quality, forever changing the way people experienced and cherished their favorite tunes.
The Rise and Fall of CDs: Exploring the Digital Revolution

In this section, we will delve into the remarkable journey of compact discs, tracing their trajectory from an innovative and widely popular music format to their eventual decline in the face of the digital revolution. We will explore how CDs transformed the way we experienced music and how they paved the way for the rise of digital music platforms.
The Science Behind CDs
In this section, we will delve into the intricate workings of compact discs and the underlying scientific principles that make them an integral part of our audio and data storage world.
Compact discs, commonly known as CDs, have revolutionized the way we store and retrieve information. They have carved their place not only in the music industry but also in the realm of data storage, offering a compact and efficient solution.
At the core of a CD lies a complex system that combines the principles of optics, laser technology, and digital data encoding. Understanding these concepts is crucial to comprehend how CDs function and why they have become indispensable in today's digital age.
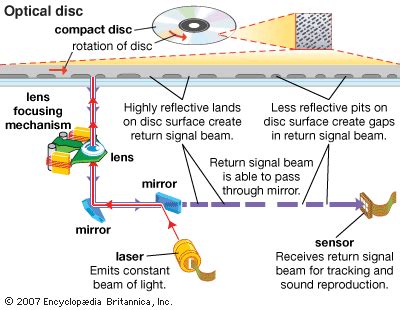
One key element is the use of lasers to read and write data on the disc's surface. Through the process of reflection and refraction, lasers interact with the microscopic pits and lands on the CD's surface, converting them into binary data. These pits and lands represent the ones and zeros of the digital code, the language that computers and CD players understand.
The CD's reflective layer is another critical component that impacts its functionality. This layer, typically made of aluminum, allows the laser to bounce off the disc's surface and reach the photodiode, which converts light signals into electrical currents. The reflection of laser light ensures accurate data reading and retrieval.
To ensure durability and protection of the data stored on a CD, various layers are employed. These layers include a protective coating to safeguard against scratches and a transparent layer that prevents interference between the laser and the reflective layer. Each layer serves a specific purpose, contributing to the overall integrity and longevity of the CD.
In conclusion, compact discs are a product of scientific ingenuity, merging principles of optics, laser technology, and digital encoding. The intricate combination of these elements allows CDs to store and retrieve vast amounts of data, making them an integral part of our audio and data storage landscape.
| Key Science Concepts |
|---|
| Optics |
| Laser technology |
| Digital data encoding |
| Reflection and refraction |
| Binary data representation |
| Reflective layer |
| Protective coating |
| Transparent layer |
How Does a CD Work? Understanding the Basics

In this section, we will delve into the inner workings of a compact disc, examining the fundamental principles behind its functionality. By gaining an understanding of the basic processes involved, we can appreciate the remarkable technology that allows CDs to store and play audio and data.
At the heart of a CD lies a reflective surface comprising tiny pits and lands, which are arranged in a spiral pattern. These pits and lands represent the encoded information that is read by a CD player. A laser beam, emitted by the player, scans the surface of the disc, reflecting off the pits and lands. The reflected light is detected and translated into electrical signals, which are then processed to produce the desired audio or data.
The laser beam employed in CD reading is of a specific wavelength, allowing it to interact with the pits and lands. When the laser shines on a land, the light is reflected back to the detector, whereas when it encounters a pit, the light scatters. This difference in reflection between pits and lands is crucial for interpreting the stored information.
- The process of encoding data onto a CD involves using a laser to etch microscopic pits into a master disc.
- The pits are then replicated onto the production discs through a stamping process.
- During playback, the laser reads the pits and lands, converting the changes in light reflection into binary code.
- This binary code is further processed to reproduce the original audio or data.
It is fascinating to realize that despite the minuscule nature of the pits and the complexity of the encoding process, CDs have been a staple medium for storing and distributing content for decades. By understanding the basics of how CDs work, we can better appreciate their enduring role in the world of digital media.
Unveiling the Secrets of Optical Data Storage
Delve into the enigmatic realm of optical data storage and unearth the concealed wonders that reside within. Explore the intricacies of this remarkable technology as we embark on a journey to unravel its mysteries and reveal the underlying mechanisms that enable it to preserve the vast amounts of information stored within its depths.
Uncovering the Mechanism
Underneath its unassuming exterior, optical data storage conceals a complex system of lasers, mirrors, and a myriad of microscopic indentations that holds the key to its functionality. This intricately designed mechanism harnesses the power of light to read and write data, seamlessly converting digital information into a tangible form that can be accessed at will.
Embracing the Laser's Ray
The centrepiece of this extraordinary technology, the laser, plays a vital role in manipulating data on the optical disc. With unparalleled precision, it emits a concentrated beam of light, allowing it to interact with the microscopic pits and lands on the disc's surface. This interaction manifests as variations in reflectivity which are read by a photodetector, ultimately converting them into the digital information that was once inscribed.
Making Sense of the Pits and Lands
A symphony of binary code, the intricate pattern of pits and lands on the disc's surface is the foundation of optical data storage. Each microscopic indentation represents a single bit of data, and as the laser traverses the disc, the photodetector meticulously deciphers these variations in reflectivity, interpreting them as strings of digital information that can be effortlessly retrieved.
Unleashing Unlimited Potential
Optical data storage has revolutionized the way we preserve and access information, providing an unparalleled level of durability and longevity. Unlike its predecessors, such as magnetic storage, optical data storage is impervious to magnetic interference and possesses the capability to withstand the test of time, ensuring the safekeeping of our invaluable data for generations to come.
Embracing the Future
As technology evolves and data generation continues to skyrocket, optical data storage remains a steadfast pillar in the realm of information preservation. Its inherent advantages, coupled with ongoing advancements, pave the way for further breakthroughs, promising even greater storage capacities and innovative applications that push the boundaries of what was once deemed possible.
Join us as we embark on this captivating exploration of optical data storage, unraveling its secrets and unveiling the remarkable potential it holds for our digital age.
The Appeal of Collecting CDs: Uncovering the Enchanting Universe of Disc Collections

In this section, we will delve into the captivating allure that surrounds the act of collecting compact discs. The world of disc collections embodies a mesmerizing realm where beauty, nostalgia, and exploration intertwine to manifest an enchanting hobby.
1. Historical Significance: Immerse yourself in the rich tapestry of history that CDs encapsulate. These silver discs, once a symbol of revolutionary technology, provide a tangible link to the past. Each CD carries a unique story, preserving the essence of an era that witnessed the transition from vinyl records to digital music. | 2. Artistic Beauty: Beyond their musical content, CDs captivate collectors with their visually stunning covers. With elaborate artwork, intricate typography, and mesmerizing designs, CD cases offer a feast for the eyes and become captivating pieces of art in their own right. |
3. Sonic Experience: Exploring a CD collection enables a unique journey through different genres, eras, and musical landscapes. The act of curating and playing these physical discs allows music enthusiasts to immerse themselves in a multisensory experience, appreciating the full spectrum of sound and relishing the rich fidelity that CDs offer. | 4. Collector's Joy: Collecting CDs brings a unique sense of joy and fulfillment to enthusiasts. Building a comprehensive collection, organizing it meticulously, and discovering hidden gems becomes a rewarding pursuit on its own. The thrill of finding rare editions or limited releases adds an element of excitement and satisfaction to the collecting journey. |
5. Sentimental Value: For many collectors, CDs hold sentimental value, representing cherished memories and personal connections. Whether it's a gift received from a loved one, a soundtrack that evokes nostalgia, or an album that defined an important phase of life, CDs serve as tangible reminders of our emotional experiences, making them all the more cherished. | 6. Exploration and Discovery: Delving into a collection of compact discs unveils a realm of endless exploration and discovery. Each new addition presents an opportunity to broaden musical horizons, stumble upon unfamiliar artists, and piece together the puzzle of an artist's discography. The process of expanding one's musical knowledge becomes an exhilarating adventure. |
The Delight of Physical Media: Exploring the Realm of CD Collecting
Within the enchanting universe of physical media lies a captivating endeavor known as CD collecting. Delving into the allure of these discs allows one to embark on a captivating journey of musical discovery, artistic appreciation, and the thrill of amassing a treasured library.
Beyond mere digital files and streaming platforms, the physicality of CDs opens up a new dimension of enjoyment. Holding a tangible CD in your hands, you can admire its intricate artwork, peruse the liner notes that accompany the music, and feel the weight of the artist’s creativity in your grasp. The act of carefully selecting CDs, organizing them on shelves, and browsing through their contents provides a tactile and immersive experience unlike any other.
CD collecting offers a unique kind of nostalgia. It evokes memories of visiting record stores, flipping through racks of albums, and stumbling upon unexpected gems. Exploring the vast and diverse world of CDs allows collectors to uncover hidden treasures, rare editions, and limited releases, all of which add a sense of exclusivity and rarity to their collection.
Furthermore, CD collecting fosters a deep appreciation for the artists and musicians behind the music. Each CD represents the culmination of their creative process, from the composition and recording to the production and mastering. By owning and actively engaging with their works on CD, collectors forge a deeper connection with the artistic expression and craftsmanship intertwined within each track.
CD collecting is also a gateway to musical exploration. It provides a tangible guide for discovering new genres, artists, and musical eras. From classical symphonies to the pulsating beats of electronic music, the vast array of CDs available allows collectors to explore a multitude of styles and broaden their sonic horizons.
In conclusion, the realm of CD collecting offers a rich tapestry of joy, nostalgia, and exploration. It celebrates the elegance of physical media, encourages a deeper appreciation for artists, and embarks collectors on an adventure of musical discovery. So venture forth, embrace the world of CD collecting, and allow yourself to be swept away in the delight of physical media.
FAQ
What is a compact disc?
A compact disc, or CD, is a flat, round disc made of plastic that is used to store and play digital audio, video, and other types of data.
Who invented the compact disc?
The compact disc was co-developed by Philips and Sony in the early 1980s. The project was led by Philips engineer Kees Schouhamer Immink.
How does a CD store information?
A CD stores information in the form of tiny pits and lands on its surface. These pits and lands are read by a laser beam in a CD player, which converts the information into sound or data.
Are CDs still popular today?
While CDs have become less popular with the rise of digital streaming and downloading, they still have a dedicated fanbase and are widely used for music, movies, and data storage.
What are some advantages of using CDs?
Using CDs offers several advantages, such as high audio quality, physical ownership of media, no reliance on internet connection or streaming services, and the ability to create personalized collections.



