The human oral cavity is an intricate ecosystem, housing a vast array of microorganisms that delicately maintain a balance. Unfortunately, this delicate harmony can be disrupted when the gum tissues become inflamed, giving rise to the potentially serious condition known as periodontal disease. This condition is characterized by the onset of various symptoms, such as gum bleeding, persistent bad breath, and eventual tooth loss.
Periodontal disorders are multifactorial in nature, arising from a culmination of diverse triggers that can influence an individual's susceptibility to this ailment. Lifestyle choices, including inadequate oral hygiene practices, smoking, and a sugary diet, can pave the way for the development of gum disease. Moreover, certain systemic conditions, such as diabetes and immune disorders, can render individuals more prone to periodontal issues.
When it comes to addressing gum disease, a multi-faceted approach is crucial for effective management. Professional dental intervention, including regular cleanings and scaling procedures, can help eliminate plaque and tartar buildup that contribute to the progression of periodontal ailments. Additionally, adopting diligent home care practices, such as regular brushing, flossing, and rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash, can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease and promote overall oral wellness.
Gum Disease: Causes and Risk Factors
The Development and Impact of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a prevalent oral condition that affects the tissues and structures supporting the teeth. This ailment can lead to severe consequences, including tooth loss, if left untreated. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with gum disease is essential to prevent its occurrence and progression.
Potential Causes of Gum Disease
Various factors can contribute to the development of gum disease. Poor oral hygiene practices, such as inadequate brushing and flossing, can lead to the accumulation of dental plaque and tartar. These substances harbor bacteria that produce toxins, triggering an inflammatory response in the gums. Additionally, smoking and tobacco use, hormonal changes in women, certain medications, and genetic predisposition can all increase the risk of gum disease.
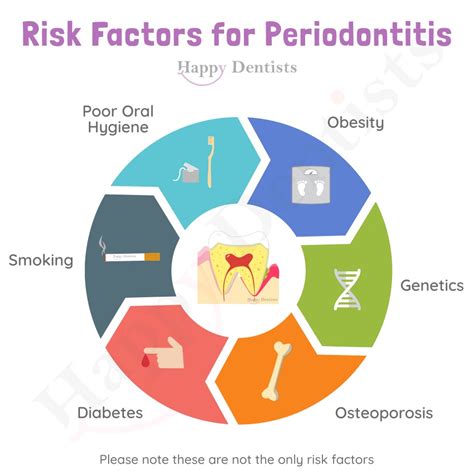
Significant Risk Factors for Gum Disease
While everyone may be susceptible to gum disease, certain individuals have a higher risk due to specific factors. Some of these risk factors include advanced age, diabetes, weakened immune system, stress, malnutrition, and obesity. Additionally, certain systemic conditions, such as HIV/AIDS and cancer, can also make a person more susceptible to gum disease.
The Dental Professionals' Role in Identifying and Addressing Risk Factors
Dental professionals play a crucial role in identifying and addressing the risk factors associated with gum disease. Regular dental check-ups enable early detection and intervention, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of gum disease. Proper oral hygiene instructions, along with personalized recommendations based on individual risk factors, can greatly contribute to maintaining optimal gum health.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes and risk factors of gum disease is vital for its prevention and management. By adopting proper oral hygiene practices, making healthy lifestyle choices, and seeking professional dental care, individuals can minimize the incidence and impact of gum disease, safeguarding their oral health for years to come.
Exploring the Factors Contributing to Periodontal Disease
Gum disease, a prevalent oral health condition, is influenced by a range of factors that contribute to its development. This section aims to delve into the various elements that play a role in the onset and progression of periodontal disease. By understanding these underlying factors, individuals can gain insight into the importance of preventive measures and targeted treatment.
- Oral Hygiene: Poor oral hygiene habits, such as irregular brushing and flossing, can lead to the accumulation of plaque and tartar. These buildups can irritate the gums and initiate the development of gum disease.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Tobacco products contain harmful chemicals that weaken the immune system and hinder proper gum tissue repair. Smoking and tobacco use are significant risk factors for periodontal disease.
- Genetic Predisposition: Certain individuals may have a higher susceptibility to gum disease due to genetic factors. These inherited traits can affect the body's response to bacteria and inflammation in the gums.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, often experienced during pregnancy or menopause, can make gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation. This hormonal imbalance can contribute to the development of gum disease.
- Medical Conditions: Certain systemic diseases, such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders, can impair the body's ability to fight infections, including gum disease. Effective management of these conditions is crucial in reducing the risk of periodontal issues.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet plays a vital role in maintaining healthy gums. Inadequate intake of essential nutrients, such as vitamin C and calcium, can weaken the immune system, making gums more susceptible to infection and periodontal disease.
- Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact the body's immune system, making it harder to combat infections and inflammation in the gums. Stress also affects individuals' oral hygiene habits, further contributing to gum disease.
By exploring these contributing factors, individuals can develop a comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted nature of gum disease. Recognizing the significance of each factor empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their oral hygiene practices and seek appropriate treatment to prevent and manage periodontal disease.
The Role of Plaque in Periodontal Concerns
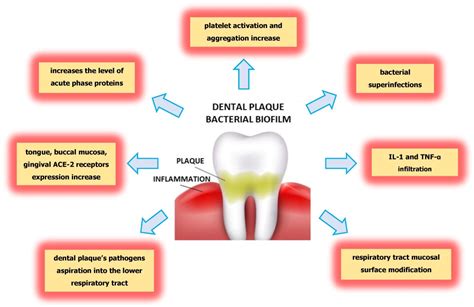
Plaque plays a significant role in the development and progression of gum disease, also known as periodontal concerns. By understanding the impact of plaque, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and treat these oral health conditions.
Plaque, a sticky and colorless film that constantly forms on the teeth, is a biofilm comprised of bacteria, food particles, and saliva. When plaque is not effectively removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can accumulate and harden into tartar or calculus, leading to inflammation of the gums.
As plaque builds up along the gumline, it releases toxins that irritate the gum tissue and trigger an immune response. Initially, this immune response manifests as gingivitis, which is characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can result in the loss of teeth and damage to the supporting structures of the mouth.
Effective plaque control is crucial in preventing and managing gum disease. Regular brushing of teeth and flossing help to remove plaque, minimizing the risk of its accumulation and the subsequent development of periodontal concerns. Additionally, professional dental cleanings and check-ups play an essential role in plaque removal and identification of any early signs of gum disease.
In summary, recognizing and addressing the role of plaque in gum disease is vital for maintaining optimal oral health. Regular oral hygiene practices, combined with professional dental care, can help individuals combat plaque accumulation and reduce the likelihood of developing periodontal concerns.
Revealing the Link between Plaque Formation and Gum Disease
In this section, we will explore the intricate relationship between the build-up of dental plaque and the development of gum disease. Understanding this connection is crucial for effectively preventing and treating gum disease.
Plaque, a sticky film composed of bacteria, food particles, and saliva, contains harmful microorganisms that can wreak havoc on the gums. When plaque is not adequately removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can accumulate along the gumline and between teeth, leading to inflammation and infection.
- Plaque Formation and Early Gum Disease:
- Link between Plaque Build-up and Gum Inflammation:
- Effects of Plaque on Gum Health:
- Preventing and Treating Gum Disease:
During the initial stages, plaque accumulation causes the gums to become red, swollen, and prone to bleeding. This condition, known as gingivitis, is a sign of early gum disease and can typically be reversed with proper oral hygiene practices.
As plaque continuously accumulates, it hardens into tartar, also called dental calculus. Tartar acts as a breeding ground for more bacteria, exacerbating gum inflammation. This chronic inflammation, known as periodontitis, is a more severe form of gum disease that can cause irreversible damage to the gums and supporting structures of the teeth.
Not only does plaque directly contribute to gum inflammation and infection, but it also triggers the body's immune response. This immune response can cause damage to the gums and surrounding tissues, leading to further deterioration of oral health.
Regular brushing and flossing, along with professional dental cleanings, are crucial for removing plaque and preventing gum disease. Furthermore, antibacterial mouthwashes and periodontal therapies may be recommended to control the bacterial load and promote gum healing.
By understanding the intricate connection between plaque formation and gum disease, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain optimal gum health and prevent the progression of oral conditions that can potentially lead to tooth loss.
Gum Disease: Signs and Symptoms
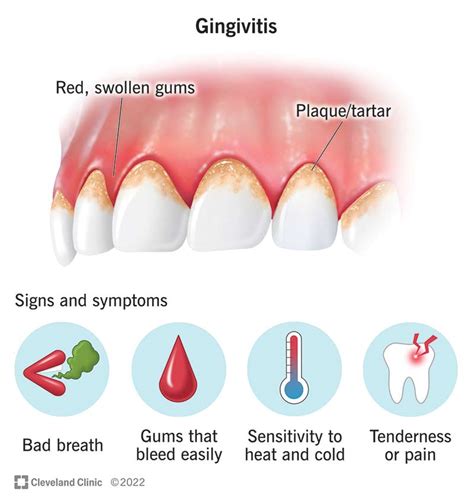
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a condition that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. This condition can be characterized by a variety of symptoms and warning signs that people should be aware of in order to prevent or seek appropriate treatment.
- Bleeding Gums: One of the most common signs of gum disease is bleeding gums. This can occur during brushing, flossing, or even when eating certain foods.
- Swollen or Tender Gums: Gums that appear swollen or feel tender to the touch may indicate the presence of gum disease. This inflammation is often a response to bacterial infection.
- Receding Gums: Over time, gum disease can cause the gums to recede or pull away from the teeth. This can lead to tooth sensitivity, as the tooth roots become exposed.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be a warning sign of gum disease. The bacteria that cause gum disease can release foul-smelling gases.
- Persistent Toothache: Gum disease can cause toothaches or tooth sensitivity, especially when the disease progresses and affects the supporting structures of the teeth.
- Pus Between Gums and Teeth: In some cases of advanced gum disease, pus may develop in the pockets formed between the gums and teeth. This is a clear indication of infection.
- Loose or Shifting Teeth: As gum disease progresses, it can cause the teeth to become loose or shift position. This is a result of the damage caused to the supporting bone and tissue.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gum disease is crucial for early detection and treatment. If you experience any of these warning signs, it is important to consult a dental professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Identifying the common signs of gum disease
Recognizing the prevalent indications of periodontal disease is crucial in maintaining good oral health and overall well-being. By familiarizing yourself with the telltale signs, you can take proactive measures to address gum disease and seek appropriate treatments if necessary.
- Bleeding gums: One of the hallmark signs of gum disease is bleeding gums, which can occur during brushing, flossing, or eating. If you notice recurring blood while performing these routine activities, it may indicate the presence of gum disease.
- Swollen or tender gums: Gum disease often leads to inflammation, causing the gums to become swollen and tender. If your gums appear puffy or feel painful to the touch, it may be a sign of underlying gum disease.
- Receding gumline: Gum recession, where the gumline pulls away from the teeth, is a common symptom of periodontal disease. This can result in teeth appearing longer or gaps forming between them.
- Persistent bad breath: Chronic bad breath that does not improve with regular oral hygiene could be a manifestation of gum disease. The bacteria in the infected gums can produce unpleasant odors.
- Loose or shifting teeth: As gum disease progresses, it can weaken the supporting structures around the teeth, causing them to become loose or shift position. If you notice changes in the alignment or stability of your teeth, it may be an indicator of gum disease.
- Painful chewing: Gum disease can lead to discomfort or pain while chewing. If you experience difficulties or pain when eating, it is advisable to consult a dental professional to evaluate the health of your gums.
Being aware of these common signs can help you identify potential gum disease early on and seek appropriate dental care. Remember, regular dental check-ups and maintaining proper oral hygiene practices are crucial in preventing and treating gum disease.
Preventing Gum Disease: Effective Oral Hygiene Practices

Your oral health is crucial in avoiding the development of gum disease and maintaining a healthy smile. By adopting effective oral hygiene practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease and its associated complications.
Brushing your teeth thoroughly at least twice a day is an essential part of a successful oral hygiene routine. The mechanical action of brushing helps remove plaque, which is a sticky film containing bacteria that can lead to gum disease. Use a soft-bristled brush and fluoride toothpaste, and make sure to clean all surfaces of your teeth, including the gumline.
Flossing is another crucial step in preventing gum disease. It helps remove plaque and food particles from areas that your toothbrush cannot reach, such as between the teeth and along the gumline. Use a gentle, sawing motion to guide the floss between your teeth, making sure to curve it around each tooth and go beneath the gumline.
Rinsing your mouth with an antibacterial mouthwash can supplement your oral hygiene routine by killing any remaining bacteria and freshening your breath. Look for a mouthwash specifically designed to target gum disease, which may contain ingredients such as chlorhexidine or essential oils.
Regular dental check-ups are vital for preventing gum disease. Your dentist will thoroughly examine your oral health and provide professional dental cleanings to remove any built-up plaque or tartar that cannot be eliminated by brushing and flossing alone. Early detection and treatment of gum disease can help prevent its progression and associated complications.
By consistently practicing these oral hygiene habits, you can take proactive steps towards preventing gum disease and maintaining optimal oral health.
Developing an Effective Oral Care Routine to Safeguard Your Gum Health
Ensuring proper oral hygiene is crucial for maintaining healthy gums and preventing the onset of gum disease. Adopting a consistent oral care routine can significantly reduce the risk of gum infections, tooth decay, and other dental problems.
Implementing a well-rounded oral care regimen involves various practices that work together to maintain optimal gum health. These practices include regular brushing, flossing, and rinsing with mouthwash. By performing each step correctly and consistently, you can effectively prevent plaque buildup, reduce the likelihood of gum inflammation, and keep your overall oral health in check.
In addition to regular dental hygiene habits, incorporating certain preventive measures can enhance the effectiveness of your oral care routine. For instance, employing a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle brushing techniques can help protect the gums from irritation or damage. Moreover, utilizing antimicrobial mouthwash can actively combat bacteria and minimize the risk of gum infections.
A balanced diet also plays a vital role in the prevention of gum disease. Consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products, can provide essential vitamins and minerals that promote gum health. Conversely, limiting the intake of sugary or acidic foods and beverages can decrease the chances of tooth decay and gum inflammation.
| Key Points: | - Regular brushing, flossing, and rinsing are vital for gum health; |
|---|---|
| - Opt for a soft-bristled toothbrush and employ gentle brushing techniques; | |
| - Incorporate antimicrobial mouthwash into your oral care routine; | |
| - Consume a balanced diet rich in vital nutrients; | |
| - Limit the intake of sugary and acidic foods and beverages. |
By diligently following a comprehensive oral hygiene routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease and maintain your oral health for years to come.
The Connection Between Periodontal Conditions and Overall Well-being

When it comes to your oral health, it's important to recognize that your gums play a crucial role in maintaining the overall well-being of your body. An interesting correlation has been established between periodontal conditions and various systemic health issues, reflecting the significant link between gum disease and overall health.
Research suggests that gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, shares a bidirectional relationship with certain medical conditions. Not only can gum disease contribute to the development of systemic diseases, but existing health conditions can also affect the health of your gums.
- Systemic Diseases Linked to Gum Disease:
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Diabetes
- Respiratory infections
- Osteoporosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
The presence of gum disease has been associated with an increased risk of developing these systemic illnesses. The inflammation and bacteria resulting from gum disease can enter the bloodstream, contributing to the progression of other health conditions. Similarly, individuals with existing systemic diseases may experience compromised gum health, as their bodies become more susceptible to infections and inflammation.
Understanding the link between gum disease and overall health is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals. Recognizing the intricate connection between oral health and systemic well-being emphasizes the importance of maintaining a healthy oral hygiene routine and seeking appropriate treatment for gum disease. By addressing gum disease, individuals can potentially reduce their risk of developing or worsening associated medical conditions.
The Impact of Gum Disease on Systemic Health
Gum disease, a common oral condition, has far-reaching effects on overall health beyond just the oral cavity. It is essential to recognize the extensive impact that gum disease can have on the body, highlighting the need for early intervention and appropriate treatment.
Severe gum disease, also known as periodontitis, can lead to a range of systemic health problems. The inflammation and infection caused by gum disease can spread throughout the body, increasing the risk of various conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and even pregnancy complications.
Research indicates that the bacteria associated with gum disease can enter the bloodstream and travel to other organs, triggering inflammatory responses and impairing their proper functioning. The chronic inflammation resulting from gum disease can exacerbate existing health conditions and weaken the body's immune response to other infections.
Moreover, gum disease has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular problems, including heart disease and stroke. The inflammation caused by gum disease may contribute to the development of fatty plaque deposits in the arteries, leading to restricted blood flow and potential blockages.
Individuals with diabetes are also particularly susceptible to the adverse effects of gum disease. Poorly controlled blood sugar levels can contribute to the progression and severity of gum disease, while gum disease can, in turn, make it more challenging to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Pregnant women with gum disease are at a higher risk of premature birth and low birth weight for their babies. The systemic inflammation triggered by gum disease can potentially affect fetal development and increase the likelihood of complications during pregnancy.
Recognizing the impact of gum disease on systemic health is crucial for both healthcare professionals and individuals themselves. Emphasizing regular dental visits, proper oral hygiene practices, and timely treatment for gum disease can help prevent its harmful consequences on overall health and well-being.
Gum Disease Treatments: Scaling and Root Planing
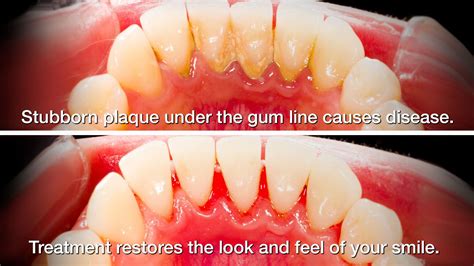
Gum disease can be effectively treated through various methods, one of which is scaling and root planing. This procedure focuses on removing plaque and tartar buildup from the teeth and their roots, helping to control the progression of gum disease and promote gum health.
Scaling involves the careful removal of plaque and tartar from the gumline and the surfaces of the teeth. It is typically performed using special dental instruments such as scalers and ultrasonic devices. By eliminating these deposits, scaling helps to reduce inflammation and prevent gum disease from worsening.
Root planing, on the other hand, specifically targets the roots of the teeth. This procedure smooths out rough areas and removes any remaining bacteria or toxins, creating a clean surface that allows the gums to reattach to the teeth. Root planing is crucial in promoting the healing of the gums and preventing further infection or damage.
Scaling and root planing are often performed together as a comprehensive treatment for gum disease. The process may require multiple appointments depending on the severity of the condition. Additionally, dental professionals may recommend the use of antimicrobial mouthwashes or antibiotics to further enhance the effectiveness of the treatment.
When performed by skilled dental professionals, scaling and root planing can significantly improve gum health and reduce the symptoms associated with gum disease. Regular professional cleanings and proper oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing, are essential in maintaining the outcomes of this treatment and preventing the recurrence of gum disease.
- Removal of plaque and tartar from the gumline and teeth
- Reduction of inflammation and prevention of gum disease progression
- Smoothing of root surfaces and removal of bacteria or toxins
- Promotion of gum healing and prevention of further infection or damage
- Comprehensive treatment requiring multiple appointments
- Enhancement of treatment effectiveness with antimicrobial measures
- Improved gum health and reduction of gum disease symptoms
- Maintenance through regular professional cleanings and proper oral hygiene
Exploring the Process of Deep Cleaning for Gum Disease Treatment
Gum disease, a common dental condition caused by various factors, can lead to serious oral health issues if left untreated. In this section, we will delve into the process of deep cleaning, a crucial treatment method for gum disease.
Deep cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing, is a professional dental procedure aimed at removing plaque and tartar buildup, thereby reducing inflammation and promoting gum health. This intensive cleaning process targets the areas below the gumline, where bacteria can cause infection and damage to the supporting structures of the teeth.
Understanding plaque and tartar:
Plaque is a sticky film that forms on the teeth and contains a mixture of bacteria, food particles, and saliva. When plaque is not effectively removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, also called calculus. Tartar buildup can irritate the gums and provide a breeding ground for harmful bacteria, leading to gum disease.
The procedure:
Deep cleaning involves two main components: scaling and root planing. During the scaling phase, a dental professional uses specialized tools to carefully remove plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces, both above and below the gumline. This meticulous process may require local anesthesia to ensure patient comfort.
Once the teeth are thoroughly scaled, the next step is root planing. This procedure smooths out the root surfaces of the teeth, making it more difficult for bacteria to adhere and allowing the gums to reattach to the teeth. Root planing also helps eliminate any remaining bacteria, further reducing the risk of infection.
The benefits of deep cleaning:
By undergoing deep cleaning, patients with gum disease can experience several benefits. This treatment not only removes harmful bacteria and promotes gum healing, but it can also help prevent tooth loss and restore the overall health of the mouth. Deep cleaning is often a crucial step in managing and halting the progression of gum disease.
In conclusion, deep cleaning plays a vital role in treating gum disease. By effectively removing plaque and tartar, this procedure allows for the reestablishment of healthy gums and prevents further damage to the teeth and supporting structures. Regular dental visits and practicing good oral hygiene are essential in maintaining optimal gum health and preventing the onset of gum disease.
FAQ
What are the common causes of gum disease?
Gum disease can be caused by poor oral hygiene, smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, genetics, and certain health conditions such as diabetes.
How can I prevent gum disease?
To prevent gum disease, it is important to brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss daily, use mouthwash, avoid smoking, eat a healthy diet, and schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings.
What are the symptoms of gum disease?
The symptoms of gum disease include red, swollen or bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, receding gums, loose teeth, and changes in the way your teeth fit together when you bite.
Can gum disease be reversed?
Early stage gum disease called gingivitis can be reversed with proper oral hygiene and professional dental treatment. However, advanced stages of gum disease called periodontitis may require more extensive treatment such as deep cleaning, medication, or even surgery.
Are there any natural remedies for gum disease?
While maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial, there are some natural remedies that may help prevent or treat gum disease, such as saltwater rinses, oil pulling with coconut oil, and using herbal mouth rinses with ingredients like chamomile or tea tree oil. However, it is always best to consult with a dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
What is gum disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that surround and support the teeth. It is caused by the bacteria in plaque, a sticky film that forms on the teeth and gums.
What are the common symptoms of gum disease?
The common symptoms of gum disease include red, swollen, and tender gums, bleeding gums while brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath, receding gums, loose teeth, and changes in the bite. It is important to consult a dentist if any of these symptoms are experienced.



