While the anticipation of motherhood can be filled with joy and excitement, it is crucial to acknowledge the potential hazards associated with partaking in spirited libations during this transformative phase of life. The act of imbibing alcoholic substances whilst carrying a child can have deleterious consequences for not only the mother but also the precious life growing within her womb that craves protection and nourishment.
Indulging in the consumption of alcoholic beverages during this critical stage places the unborn baby at a heightened risk of enduring a myriad of adverse outcomes. Exposing the developing fetus to the perils of alcohol can engender a host of developmental abnormalities and impairments that may persist well beyond the prenatal period. The profound influence of these potent substances can disrupt the delicate stages of embryonic and fetal growth, leading to a cascade of irreversible physiological and neurological complications.
It is imperative to comprehend the grave implications that ensue when one unwittingly exposes their unborn child to intoxicating brews. By disregarding the persuasions of medical professionals and discarding the cautionary advice disseminated by trusted sources, individuals place their unborn progeny in jeopardy of enduring lifelong ramifications. Understanding the insidious nature of this insidious indulgence is paramount in safeguarding the well-being and future of the child, empowering women to make informed decisions and adopt a lifestyle free from the potential harm of alcohol consumption during this pivotal period.
Risks Associated with Consuming Alcohol While Pregnant

Alcohol consumption during pregnancy poses multiple hazards to the developing fetus. The detrimental effects of consuming alcoholic beverages while pregnant can have far-reaching consequences for the unborn baby's health and well-being. It is crucial for expectant mothers to be aware of these risks and make informed decisions to protect the future of their child.
- Adverse effects on fetal development: Alcohol exposure during pregnancy can disrupt the normal development of the fetus, leading to physical, cognitive, and behavioral impairments in the child.
- Increased risk of birth defects: Consuming alcohol during pregnancy increases the chances of the baby being born with structural or functional abnormalities, such as heart defects, facial deformities, or learning disabilities.
- Higher likelihood of miscarriage or stillbirth: Pregnant women who drink alcohol are at a greater risk of experiencing pregnancy loss, including miscarriage or stillbirth.
- Developmental delays and learning difficulties: Alcohol can negatively impact the baby's brain development, resulting in long-term consequences such as developmental delays, learning difficulties, and decreased intellectual functioning.
- Behavioral and emotional problems: Children exposed to alcohol in the womb are at an increased risk of developing behavioral and emotional problems, including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), aggression, and difficulties with self-regulation.
- Increased vulnerability to substance abuse: The exposure to alcohol prenatally may predispose the child to a higher susceptibility to alcohol and substance abuse later in life.
Given the numerous risks associated with alcohol consumption during pregnancy, it is imperative for women who are expecting or planning to conceive to abstain from drinking alcohol. The potential harm to the unborn child far outweighs any momentary pleasure or social pressure that may arise from consuming alcoholic beverages. It is advisable for pregnant women to seek support from healthcare professionals, attend prenatal care visits regularly, and make informed choices to ensure the best possible outcomes for their child's health and development.
The Risks and Consequences for the Developing Baby
When a mother consumes alcoholic beverages while pregnant, it can lead to a multitude of potential hazards and unfavorable outcomes for the developing baby. The ingestion of these substances during gestation poses a substantial threat to the unborn child and can result in detrimental effects on their overall health and well-being.
Adverse Effects on Growth and Development:
The consumption of alcohol during pregnancy can impede the normal growth and development of the fetus. It can contribute to stunted physical growth and lead to a variety of cognitive and behavioral impairments in the child. The impact of maternal alcohol consumption on the developing baby's brain can result in long-lasting consequences, affecting their learning abilities and overall intellectual functioning.
Teratogenic Effects:
Exposure to alcohol in utero increases the risk of various birth defects, known as teratogenic effects. These defects can range from structural abnormalities, such as heart defects or facial malformations, to functional impairments, including difficulties with vision or hearing. The severity and type of defects can vary depending on the timing and amount of alcohol consumed during pregnancy.
Neurological Impairments:
Alcohol consumption during pregnancy can cause irreversible damage to the developing baby's nervous system, resulting in a range of neurological impairments. These can manifest as difficulties with motor skills, coordination, and balance. Additionally, the child may experience issues with attention, memory, and information processing, affecting their academic performance and overall quality of life.
Behavioral and Emotional Challenges:
The impact of maternal alcohol consumption on the unborn child can extend beyond physical and cognitive impairments and affect their emotional and behavioral well-being. Children exposed to alcohol during gestation are at a higher risk of developing behavioral problems, such as hyperactivity, impulsivity, and difficulties with self-regulation. They may also struggle with emotional regulation, leading to increased rates of anxiety, depression, and aggression as they grow older.
Lifetime Consequences:
The risks and consequences of maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy can have long-lasting effects throughout the child's life. Even if the physical abnormalities are not immediately apparent, the cognitive, behavioral, and emotional challenges can persist into adolescence and adulthood. It highlights the importance of raising awareness about the dangers of consuming alcohol while pregnant and implementing strategies to prevent fetal alcohol syndrome.
In conclusion, the risks and consequences for the developing baby due to maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy are far-reaching and can have a lasting impact on their physical and psychological well-being. It reinforces the crucial need for expectant mothers to refrain from alcohol consumption during this critical period to safeguard the optimal development and potential of their precious unborn child.
Impact of Alcohol on Fetal Development
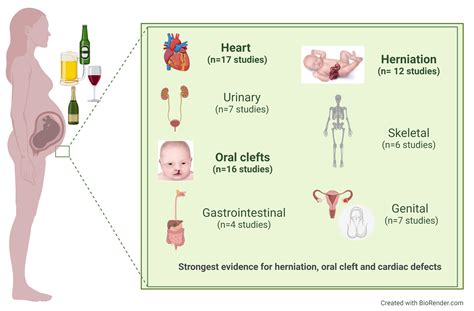
Alcohol consumption by expectant mothers can have significant negative effects on the development of their unborn child. The use of alcohol during pregnancy can result in detrimental consequences for the growth and well-being of the fetus.
- 1. Impaired Brain Development: The consumption of alcohol during pregnancy can hinder the proper development of the fetal brain, potentially leading to cognitive and behavioral disorders later in life.
- 2. Physical Deformities: Alcohol exposure in utero can cause a range of physical abnormalities in the unborn child, including facial deformities, heart defects, and growth restrictions.
- 3. Organ Dysfunction: The developing organs of the fetus are especially vulnerable to the negative impact of alcohol. Liver damage, kidney dysfunction, and compromised immune system function are all potential consequences.
- 4. Neurobehavioral Issues: Alcohol's influence on fetal development can result in neurobehavioral issues such as learning difficulties, poor impulse control, and attention deficits.
- 5. Increased Risk of Miscarriage: Expectant mothers who consume alcohol during pregnancy have a higher risk of experiencing miscarriage or stillbirth, further emphasizing the importance of abstaining from alcohol.
In conclusion, alcohol consumption during pregnancy can exert profound effects on the development of the unborn child. It is crucial for expectant mothers to prioritize the well-being of their baby by completely avoiding alcohol to minimize the potential harm it can cause.
Negative Consequences on the Physical and Cognitive Development of Offspring
When a mother consumes substances that have the potential to harm her unborn child, there can be detrimental consequences on both the physical and cognitive development of the offspring. These substances can adversely affect the growth and functioning of various body systems, leading to a range of short-term and long-term negative effects that can persist throughout the child's life.
- Impaired Physical Growth: Maternal consumption of harmful substances during pregnancy can hinder the normal growth and development of the fetus. It may result in low birth weight, stunted growth, and physical abnormalities. These physical impairments can have long-lasting effects on the child's overall health and well-being.
- Neurological Damage: The developing brain of the unborn child is particularly vulnerable to the negative effects of maternal substance consumption. Exposure to harmful substances can disrupt the formation of neural connections, leading to cognitive impairments, learning difficulties, and behavioral problems later in life.
- Developmental Delays: Prenatal exposure to substances can interfere with the chronological progression of developmental milestones. The child may experience delays in motor skills, language acquisition, and social-emotional development, resulting in significant challenges during early childhood and beyond.
- Increased Risk of Mental Health Disorders: Research has shown a link between maternal substance abuse during pregnancy and an increased risk of mental health disorders in the offspring. Conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety, depression, and addiction may manifest during childhood or adolescence.
- Higher Susceptibility to Substance Abuse: Children who were exposed to harmful substances in the womb are more likely to develop a vulnerability to substance abuse themselves. This heightened susceptibility is thought to be due to genetic and environmental factors that interact to increase the risk of substance use disorders.
In conclusion, the negative consequences of maternal substance consumption during pregnancy can significantly impact the physical and cognitive development of the child. By understanding these risks, it becomes crucial to educate expectant mothers about the importance of abstaining from substances that could harm the unborn child, thereby promoting a healthier start to life.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: A Lifelong Burden

Exposing a developing fetus to the detrimental effects of maternal substance consumption during pregnancy can have grave, enduring ramifications on the child's physical, cognitive, and behavioral development. This section sheds light on the devastating consequences of an unborn child being subjected to the perils of maternal alcohol consumption.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) constitutes a profound and enduring condition that arises from prenatal exposure to alcohol. The impact of this syndrome reverberates throughout an individual's entire lifespan, presenting a myriad of challenges that significantly impede their overall well-being. The lifelong burden carried by those affected by FAS exemplifies the far-reaching consequences that can result from maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
Physical Impairments: FAS manifests in a range of physical abnormalities that can profoundly hinder an individual's physical functioning. These may include craniofacial abnormalities, such as distinctive facial features, impaired growth and development, and malformations of the heart, kidneys, and bones. These physical impairments not only affect an individual's appearance but also have lasting implications for their health and ability to engage in daily activities.
Cognitive Deficits: Beyond the visible physical manifestations, FAS exacts a heavy toll on an individual's cognitive abilities. Children affected by FAS often experience learning difficulties, memory deficits, and challenges with problem-solving and decision-making. These cognitive deficits can severely hamper educational attainment and hinder their ability to acquire essential life skills, perpetuating long-term disadvantages.
Behavioral Challenges: FAS also gives rise to a range of behavioral issues that can persist into adulthood. Individuals with FAS frequently exhibit impulsivity, hyperactivity, and difficulties with emotional regulation. These behavioral challenges can significantly impact their relationships and social interactions, impeding their ability to form and maintain meaningful connections with others.
In conclusion, Fetal Alcohol Syndrome represents a lifelong burden that encompasses physical impairments, cognitive deficits, and behavioral challenges. Maternal consumption of alcohol during pregnancy can cause irreversible damage to the unborn child, underscoring the importance of raising awareness about the dangers of alcohol consumption during this critical period.
The Long-Term Consequences for Offspring Exposed to Maternal Prenatal Alcohol Consumption
Prenatal exposure to alcoholic beverages can have significant and lasting effects on the development and well-being of children in the long term. Maternal consumption of alcohol during pregnancy can lead to a range of adverse outcomes for the offspring, influencing various aspects of their physical, cognitive, and behavioral development.
Research suggests that individuals exposed to alcohol in the womb may experience a higher risk of developing certain physical abnormalities, such as facial dysmorphology and growth deficiencies. These effects are commonly associated with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs), a group of conditions that can have lifelong implications for affected individuals.
Cognitive impairments are also frequently observed in children exposed to maternal prenatal alcohol consumption. These may manifest as learning difficulties, impaired executive functioning, reduced intellectual abilities, and problems with attention and memory. Such cognitive deficits can impact academic performance, hinder social interactions, and limit future opportunities for affected individuals.
Furthermore, behavioral issues are often prevalent in children exposed to alcohol in utero. These may include hyperactivity, impulsivity, aggression, and difficulties with emotional regulation. Such behavioral challenges can present significant obstacles to family dynamics, peer relationships, and overall mental health.
The long-term consequences of prenatal alcohol exposure go beyond the individual affected and can have broader societal implications. The financial burden associated with providing necessary support and interventions for affected individuals can be substantial. Additionally, the emotional toll on families and communities can be significant, as they navigate the challenges and complexities associated with raising and supporting children affected by prenatal alcohol exposure.
It is essential for expectant mothers and healthcare providers to recognize the potential long-term consequences of maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy. Raising awareness, promoting prevention strategies, and providing appropriate support are crucial steps towards mitigating the negative impacts and improving the outcomes for these vulnerable individuals.
FAQ
Can drinking alcohol during pregnancy harm the unborn child?
Yes, drinking alcohol during pregnancy can harm the unborn child. It can lead to a range of serious birth defects and developmental disorders known as fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs).
How much alcohol is safe to consume during pregnancy?
No amount of alcohol is considered safe during pregnancy. Even small amounts of alcohol can pose a risk to the developing fetus.
What are the potential consequences of drinking alcohol during pregnancy?
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy can cause physical abnormalities, growth problems, learning disabilities, behavioral problems, and intellectual disabilities in the unborn child.
Are there any safe alternatives to alcohol during pregnancy?
Yes, there are plenty of safe alternatives to alcohol during pregnancy. Non-alcoholic mocktails, fruit juices, herbal teas, and flavored water can be enjoyed instead of alcoholic beverages.
Why is it important for pregnant women to completely abstain from alcohol?
It is crucial for pregnant women to completely abstain from alcohol because the developing fetus does not have the ability to metabolize alcohol like adults do. Any amount of alcohol can have damaging effects on the baby's brain and development.
What are the dangers of drinking alcohol during pregnancy?
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy can cause a variety of dangers for the unborn child. It increases the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, and premature birth. It can also lead to fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) which can cause physical, behavioral, and intellectual disabilities in the child.



