Delving into the realm of nurturing small creatures, individuals find themselves immersed in a captivating world where unconventional farming practices take center stage. This extraordinary realm, often unexplored by the masses, unveils a plethora of unique opportunities that have the potential to revolutionize the future of agriculture. Stepping away from conventional notions of farming, certain enthusiasts have discovered the mesmerizing art of rearing insects - a practice that bewitches the curious minds and ignites a new wave of sustainable food production.
Within this extraordinary universe, an array of captivating life cycles unfolds, showcasing the remarkable diversity and resilience of these minuscule beings. The intricacies of their metamorphosis, the resilience they exhibit in the face of adversity, and their valuable contribution to the ecosystem are just a few aspects that make these creatures immensely fascinating. With each species boasting its own story, individuals who venture into this realm find themselves enthralled by the secrets these tiny organisms have to offer.
The world of insect cultivation nurtures a profound appreciation for the delicate balance that exists within nature. It presents a stunning panorama of interconnectedness as these tiny life forms play essential roles in pollination, waste decomposition, and pest control. Through the careful cultivation of insects, enthusiasts aim to harness the untapped potential of these creatures, fostering a sustainable and harmonious coexistence between humans and nature. By embracing this unconventional farming practice, individuals embark upon an enchanted journey that combines scientific exploration, environmental stewardship, and innovative culinary possibilities.
The Intriguing Universe of Rearing Larvae: Experiencing the Allure of Bug Cultivation
Embark on a remarkable journey into the enthralling realm of insect farming, where nature's miniature marvels hold boundless potential. Delve deep into the captivating process of nurturing and rearing an array of mesmerizing insect larvae, unveiling a world teeming with vital ecological significance and a plethora of untapped opportunities.
- Unveiling Nature's Delectable Treasures: Revealing the awe-inspiring diversity of edible insect larvae
- Revolutionary Solutions for Sustainable Protein Production: Exploring the untapped potential of insect farming in addressing global food security challenges
- Harmony in Waste Management: Witnessing the transformative power of maggot cultivation in organic waste recycling
- Captivating Applications in Medicine and Research: Unraveling the extraordinary contribution of insect farming to pharmaceutical advancements and scientific breakthroughs
- An Eco-Entrepreneur's Paradigm: Unleashing the entrepreneurial opportunities in insect farming and the burgeoning market demand
- Unlocking the Secrets of Nature's Most Efficient Detoxifiers: Discovering how insect farming provides an environmentally friendly solution for bioremediation
Immerse yourself in the enchanting world of insect farming, where fascination intertwines with sustainability, science, and a deep appreciation for the intricate wonders of nature. Join the forefront of this burgeoning industry and embrace the endless possibilities that cultivating these extraordinary creatures can offer.
The Emergence of Bug Agriculture: a Growing Phenomenon in the Farming Sector
In recent years, an unconventional trend has been steadily gaining traction in the agricultural industry. A new and exciting practice, often dubbed as bug agriculture, is on the rise. This emerging field involves the cultivation and utilization of small invertebrate creatures as both a sustainable food source and a means of addressing various environmental challenges. With its potential to contribute to global food security and promote ecological balance, bug agriculture is capturing the attention of farmers, scientists, and entrepreneurs alike.
The Sustainable Solution: Bug agriculture offers a unique and alternative approach to traditional farming methods. By raising and breeding insects for consumption or other applications, it presents a sustainable solution to address issues such as dwindling resources, climate change, and food scarcity. Insects have a remarkable ability to convert organic waste into high-quality protein, making them an efficient and eco-friendly option for animal feed and human food production. This emerging trend is not only environmentally responsible but also economically viable, as it requires minimal space, water, and feed compared to traditional livestock farming.
Exploring the Versatility: Bug farming encompasses a wide range of insect species, each with its distinct qualities and potential applications. From commonly known edible insects like crickets and mealworms to lesser-known varieties such as black soldier flies and waxworms, the possibilities are vast. These critters can be processed into various forms, including powders, oils, or whole insects, to be used in an array of products such as protein bars, pet food, and even skincare items. Furthermore, the byproducts of bug cultivation, such as nutrient-rich frass and biofertilizers, can contribute to sustainable agriculture practices and soil health improvement.
Overcoming Challenges: While bug agriculture holds immense promise, it also presents significant challenges. Regulatory frameworks and societal acceptance are among the hurdles that need to be addressed. Striking a balance between scaling up production and maintaining ethical conditions for insects also requires careful consideration. However, with ongoing research, advancements in technology, and an increasing understanding of the potential benefits, the insect farming industry is steadily gaining traction.
In conclusion, the emergence of bug agriculture as an expanding trend in the agricultural industry offers a fresh perspective on sustainable food production and environmental stewardship. The cultivation of insects provides a versatile and efficient solution to address global challenges, while also presenting opportunities for economic growth and innovation. As this promising industry continues to evolve, it is crucial to promote dialogue, collaboration, and education to maximize the benefits of bug farming for a more sustainable future.
Maggots as Sustainable Protein: Exploring the Nutritional Value and Environmental Benefits

Unlocking the potential of an often-overlooked natural resource, maggots offer a compelling solution to both the global demand for protein and the urgent need for sustainable farming practices. This section delves into the nutritional composition of maggots and their positive impact on the environment.
1. Rich Protein Profile:
- High in essential amino acids
- Abundant source of essential fatty acids
- Significant presence of vitamins and minerals
- Complete and well-balanced source of nutrients
2. Low Environmental Impact:
- Minimal land requirements for maggot farms
- Significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional livestock farming
- Reduced use of water, feed, and pesticides
- Optimal resource efficiency through organic waste conversion
3. Promotes Circular Economy:
- Utilizes organic waste as a nutrient source
- Contributes to the reduction of food waste
- Supports the creation of a sustainable and self-sufficient farming system
- Provides an opportunity for local economic development through insect farming
Embracing the edible potential of maggots not only offers a sustainable and nutrient-rich protein source but also presents a promising solution for the challenges faced by conventional farming practices. By exploring the nutritional value and environmental benefits of maggots, we can pave the way towards a more sustainable and resilient food system for future generations.
Contributing to Circular Economy: Transforming Organic Waste into a Sustainable Food Source through Insect Farming
As societies become increasingly aware of the need for sustainable solutions to feed a growing global population, the concept of insect farming has gained significant attention. This innovative practice involves harnessing the natural abilities of insects to convert organic waste into a valuable food source, thus contributing to the principles of the circular economy.
Insect farming presents a unique opportunity to address two major challenges faced by our society: the management of organic waste and the sustainable production of food. By utilizing insects as efficient and effective bioconverters, organic waste materials that would typically end up in landfills can be transformed into a nutrient-rich feed for insects. In turn, these insects can be cultivated and harvested for their valuable proteins, oils, and other nutritional components.
The potential of insect farming lies in its ability to close the loop in the circular economy by creating a self-sustaining system. Unlike traditional farming methods, which require large amounts of land, water, and energy, insect farming can be done in controlled environments with minimal resource consumption. Insects such as mealworms, black soldier flies, and crickets have proven to be particularly efficient at converting organic waste into high-quality protein sources, making them a promising alternative to traditional livestock farming.
- Reducing waste: Insect farming helps to divert organic waste from landfills, reducing the environmental impact associated with waste disposal and methane emissions.
- Conserving resources: In contrast to conventional livestock farming, insect farming requires significantly less land, water, and feed, making it a more sustainable option for food production.
- Enhancing biodiversity: By incorporating insects into the food system, we can diversify our protein sources and reduce the ecological strain caused by mono-cropping and industrial livestock farming.
- Promoting economic growth: Insect farming holds the potential to create new job opportunities and boost rural economies, particularly in regions where organic waste management is a pressing issue.
- Engaging in innovative research: The field of insect farming is continuously evolving, with ongoing research focusing on optimizing breeding techniques, exploring novel insect species, and developing scalable technologies for large-scale production.
As we strive for a more sustainable future, insect farming emerges as a promising solution for transforming organic waste into a valuable food source. By embracing this practice, we can harness the natural abilities of insects to contribute to a circular economy, reduce waste, conserve resources, and create a more sustainable and resilient food system for all.
The Art of Maggot Farming: Insights into the Techniques and Methods

In this section, we explore the intricacies and secrets behind the captivating practice of rearing and nurturing maggots. Delving into the realm of entomoculture, we uncover the various methodologies and approaches employed by dedicated enthusiasts in the pursuit of this unique agricultural endeavor.
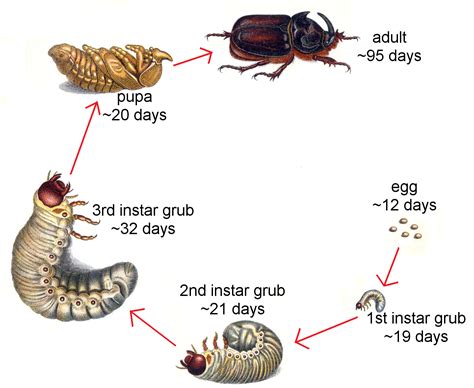
Understanding the Lifecycle:
Before embarking on the journey of maggot farming, it is crucial to comprehend the life cycle of these remarkable creatures. By gaining insights into the various stages they undergo, from egg to larva to pupa, we can better appreciate the delicate balance required in their cultivation.
Creating the Optimal Environment:
Successful maggot farming necessitates the development of a carefully controlled habitat. From temperature regulation to moisture levels, every element plays a vital role in ensuring optimal conditions for their growth and development. We explore the techniques utilized to achieve the perfect balance, allowing these tiny creatures to thrive.
Choosing the Ideal Substrate:
The selection of the appropriate substrate is paramount to the success of any maggot farm. We delve into the various options available, exploring the benefits and drawbacks of each. From organic matter to animal waste, different substrates offer unique qualities that cater to specific maggot cultivation objectives.
Nurturing Methods and Feeding:
Discover the diverse practices employed by maggot farmers to provide their larvae with a nutrient-rich diet. From supplementing their diet with specific organic materials to innovative feeding techniques, these insights shed light on the art of optimizing the growth and nutritional value of maggots.
Harvesting and Utilization:
Finally, we explore the methods employed to harvest and utilize the harvested maggots. Whether for culinary purposes, animal feed, or bioconversion, understanding the techniques for safely harvesting and utilizing these creatures allows enthusiasts to embrace the full potential of maggot farming.
Embark on this captivating journey as we delve into the art, science, and practicality of maggot farming, revealing the extraordinary world of these industrious creatures.
Beyond Maggots: Exploring the Diversity of Insects Cultivated for Food and Other Purposes
In addition to the popular option of cultivating maggots, the world of insect farming offers a vast array of fascinating possibilities for food production and other purposes. This emerging industry is driven by the recognition of insects' unique nutritional content, environmental sustainability, and their potential to address food security challenges.
One significant category of insects cultivated for food is edible beetles. These small creatures, with their exoskeletons and six legs, are rich in protein and essential nutrients. Beetle larvae, such as mealworms and buffalo worms, are commonly utilized in various culinary dishes. They can be transformed into flour, used as a protein supplement, or incorporated into a wide range of recipes, including baked goods, snacks, and protein bars.
Another intriguing group of insects for cultivation is crickets. These chirping insects are packed with nutrients like iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. The versatility of crickets in the culinary world is evident in their transformation into protein-rich powders or flours, which can be used for cooking and baking purposes. Additionally, whole crickets can be roasted, flavored, or ground into meal, offering a crunchy and sustainable alternative to traditional snacks.
The realm of edible insects extends beyond beetles and crickets. Grasshoppers, for instance, offer a unique flavor profile, high-protein content, and a low environmental impact. Their versatility in cuisine is showcased through the creation of protein-rich snacks, energy bars, and even condiments like cricket-infused sriracha sauce. Furthermore, silkworm pupae, with their creamy texture and delicate taste, are highly valued in some cultures and used in traditional dishes and snacks.
Beyond food production, the world of insect farming holds potential for various other purposes. For instance, the medicinal value of insects has been explored, with compounds extracted from certain species showing promise in the development of novel pharmaceuticals. Additionally, insects can be cultivated for their valuable byproducts, such as fertilizers derived from their waste, or for their contribution to waste management through their ability to efficiently consume organic matter.
In conclusion, while maggots may be a popular focus in the world of insect farming, there is a vast range of diverse insects that can be cultivated for food and other purposes. From edible beetles and crickets, to grasshoppers and silkworm pupae, the potential of this industry extends far beyond our conventional thinking. Embracing the nutritional benefits, environmental sustainability, and versatility of these insects may pave the way for a more sustainable and innovative future in food production and beyond.
Insect Farming: Addressing Global Food Security Challenges and Embracing New Opportunities

Introduction: As our world population continues to grow at an unprecedented rate, ensuring food security for all becomes a crucial challenge. Insect farming emerges as a promising and innovative solution that offers a plethora of opportunities to overcome this pressing issue. By exploring the untapped potential of insects, we can revolutionize our approach to food production and create sustainable solutions that address global hunger.
Challenges in Scaling Insect Farming: While the concept of insect farming holds tremendous potential, it also presents various challenges that need to be addressed. One major obstacle is the societal perspective on insects as a food source. Overcoming deeply rooted cultural biases and misconceptions, and raising awareness about the nutritional and environmental benefits of edible insects is essential. Additionally, establishing proper regulations, ensuring food safety standards, and developing efficient farming practices are critical for successful large-scale insect farming.
Opportunities for Sustainable Food Production: Insect farming offers unique opportunities to enhance our current food production systems. Unlike traditional livestock, insects require significantly less land, water, and feed resources. They also have a rapid reproduction rate and can be farmed in vertical or controlled environments, making them ideal for urban areas. Insects have a high nutritional value, containing essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. By incorporating insects into our diets, we can improve the nutritional quality of the food we consume and reduce the strain on traditional agriculture.
Environmental Benefits: Insect farming presents a sustainable alternative that addresses the environmental challenges associated with conventional livestock farming. Insects emit fewer greenhouse gases, consume less water, and produce less waste compared to traditional livestock. By shifting towards insect farming, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint and mitigate the negative environmental impacts caused by intensive farming practices.
Economic Opportunities: Insect farming not only offers solutions to global food security but also opens up new economic prospects. The growing demand for edible insects creates opportunities for job creation and entrepreneurship. Insect-based products, such as protein powders, snacks, and animal feed, have gained popularity in the market, providing avenues for economic growth and diversification.
Conclusion: Insect farming represents a paradigm shift in our approach to food production, offering a sustainable and versatile solution to global food security challenges. By embracing the potential of insect farming, addressing the associated challenges, and capitalizing on the opportunities it presents, we can pave the way for a more resilient and sustainable future for all.
FAQ
Why would anyone want to cultivate maggots?
Maggots have a variety of uses and applications. They are commonly used in forensics, medical research, waste management, and animal feed production. Cultivating maggots allows for a sustainable and efficient production process, making it a viable option for these industries.
What are the benefits of insect farming?
Insect farming offers numerous benefits. Firstly, insects are highly nutritious and rich in proteins, making them an excellent source of food. Additionally, insect farming requires significantly less land, water, and feed compared to traditional livestock farming, reducing environmental impact. Insect farming also has the potential to create economic opportunities and provide employment in rural areas.
How are maggots farmed?
Maggots are typically farmed using organic waste materials, such as food scraps or manure. These waste materials are placed in controlled environments, such as fermenters or compost bins, where they attract flies that lay eggs. The eggs hatch into maggots, which then feed on the waste material. The maggots are harvested and processed accordingly for their specific use.
What are some common challenges in insect farming?
Insect farming faces several challenges. Regulations and legal frameworks surrounding insect farming vary across countries, which can hinder the industry's growth. Developing efficient and cost-effective farming methods is also a challenge, as well as scaling up production to meet increasing demands. Additionally, consumer acceptance and awareness of insect-based products can influence market demand.
Are maggots safe for human consumption?
Yes, when properly reared and processed, maggots are safe for human consumption. They are thoroughly cleaned and sterilized before being used as food ingredients. However, it is important to ensure that maggots are sourced from reputable and regulated insect farms to guarantee their safety and quality.
Why would anyone want to farm maggots?
There are several reasons why someone would want to farm maggots. Maggots are actually a highly nutritious source of protein, and they can be used as feed for livestock such as chickens and fish. They are also used in certain industries, such as pharmaceuticals and waste management. Additionally, maggot farming is a sustainable and environmentally friendly practice that can help reduce food waste.



